Home > Press > Nanoparticle breakthrough could improve solar cells
 |
| Precision-crafted nanoparticles could enable photovoltaic cells to harness a much bigger chunk of the sun’s energy. |
Abstract:
The sun may soon power many more homes and appliances, thanks to chemists at Idaho National Laboratory and Idaho State University. They have invented a way to manufacture highly precise, uniform nanoparticles to order. The technology, which won an R&D 100 Award this year, has the potential to vastly improve photovoltaic cells and further spur the growing nanotech revolution.
Nanoparticle breakthrough could improve solar cells
Idaho Falls, ID | Posted on October 29th, 2009INL chemist Bob Fox and his ISU colleagues were looking for a better way to make semiconducting nanoparticles for solar cells. When the researchers introduced "supercritical" carbon dioxide — CO2 that behaves like both a gas and a liquid — to their reactions, they generated high-quality nanoparticles at low, energy-saving temperatures. And, surprisingly, the nanoparticles were incredibly uniform.
With subsequent tweaking, the team figured out how to make nanoparticles of prescribed sizes — anywhere from 1 to 100 nanometers — with unprecedented precision. Because the properties of nanoparticles are so strongly size-dependent, the implications of this breakthrough are vast.
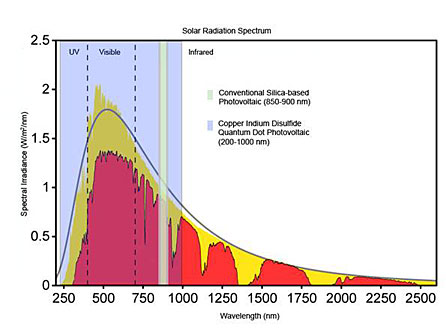
The new methodology could lead to more efficient solar cells, for example. Photovoltaic cells generate electricity when incoming photons knock electrons loose from atoms of a semiconducting material. The energy required to free these electrons — called the band gap — is specific to each material and corresponds to a mere sliver of the sun's radiation spectrum. Lower-energy photons do nothing, and the extra punch of higher-energy photons is wasted as heat. This fact explains why the efficiency of most current cells maxes out around 20 percent.
But more of the sun's energy could be captured if semiconductor building blocks could be tuned to several specific wavelengths of light. The band gap of semiconducting nanoparticles changes greatly with size, so precise control of nanoparticle dimensions may make it possible to manufacture such building blocks from a single material. A photovoltaic cell made of such components could capture huge swathes of the solar energy spectrum.
Other, similar applications should soon appear on the horizon for the technology, which has been licensed by Precision Nanoparticles, Inc., of Seattle.
"The only thing limiting us at this point is our imagination," Fox says.
####
About Idaho National Laboratory
In operation since 1949, INL is a science-based, applied engineering national laboratory dedicated to supporting the U.S. Department of Energy's missions in nuclear and energy research, science, and national defense.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Idaho National Laboratory
2025 Fremont Avenue
Idaho Falls, ID 83415
866-495-7440
Copyright © Idaho National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








