Home > Press > Building a better qubit
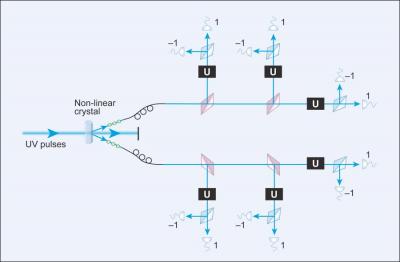 |
| A new method for combining six photons together results in a highly robust qubit capable of transporting quantum information over long distances. |
Abstract:
Combining 6 photons together results in highly robust qubits
Building a better qubit
Washington, DC, Sweden and Poland | Posted on October 7th, 2009Exploiting quantum mechanics for transmitting information is a tantalizing possibility because it promises secure, high speed communications. Unfortunately, the fragility of methods for storing and sending quantum information has so far frustrated the enterprise. Now a team of physicists in Sweden and Poland have shown that photons that encode data have strength in numbers. Their experiment is reported in Physical Review Letters and Physical Review A and highlighted in the October 5 issue of Physics (physics.aps.org).
In classical communications, a bit can represent one of two states - either 0 or 1. But because photons are quantum mechanical objects, they can exist in multiple states at the same time. Photons can also be combined, in a process known as entanglement, to store a bit of quantum information (i.e. a qubit).
Unlike data stored in a computer or typically sent through conventional fiber optic cables, however, qubits are extremely fragile. A kink in a cable, the properties of the cable material, or even changes in temperature can corrupt a qubit and destroy the information it carries. But now a group lead by Magnus Rådmark at Stockholm University has shown that six entangled photons can encode information that stands up to some knocking around.
Rådmark and his team proved experimentally that their six photon qubits are robust and should be able to reliably carry information over long distances. The technology to encode useful information on the qubits and subsequently read it back is still lacking, but once those problems are solved, we will be well on our way to secure, reliable, and speedy quantum communication.
Also in Physics: Quasiparticles do the twist
Joel Moore writes a Viewpoint on a paper examining the experimental evidence for oddball particles that don't behave like either fermions or bosons, the two breeds of particles in quantum mechanics.
####
About American Physical Society
APS Physics: APS Physics publishes expert written commentaries and highlights of papers appearing in the journals of the American Physical Society. Here are some of the papers that will be featured in this week's issue of APS Physics.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
James Riordon
301-209-3238
American Physical Society
Copyright © Eurekalert
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








