Home > Press > Novel polymer delivers genetic medicine, allows tracking
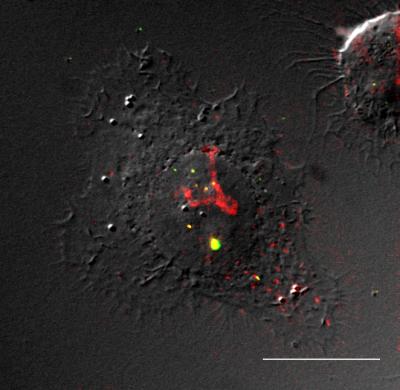 |
| Researchers at Virginia Tech and at the University of Cincinnati designed novel polymeric beacons capable of delivering plasmid DNA into mammalian cells. This image shows a deconvoluted micrograph of a HeLa cell transfected with DNA-polymer beacon complexes. The DNA is labeled with fluorescein isothiocyanate and appears green in the image. Eu3+ luminescence from the polymeric beacon appears red. Yellow pixels can be qualitatively used to visualize regions of co-localization of DNA and polymer beacon. The DNA and polymer beacon signals are overlaid with the DIC image to show contrast and morphology of the cell (scale bar = 20 micrometers).
Credit: Image provided by Joshua Bryson. |
Abstract:
Theresa M. Reineke, associate professor of chemistry in the College of Science, and colleagues in her lab at Virginia Tech and at the University of Cincinnati have developed a new molecule that can travel into cells, deliver genetic cargo, and packs a beacon so scientists can follow its movements in living systems.
Novel polymer delivers genetic medicine, allows tracking
Blacksburg, VA | Posted on October 6th, 2009"My lab has been trying to find a way to deliver genetic-based drugs into cells." said Reineke.
Scientists worldwide are using information from the human genome project as an approach to treat disease. Reineke's focus is cancer and cardiovascular disease. "Traditional drugs are aimed at treating disease at the protein level," she said. "Genetic drugs - such as those that can alter or control gene expression - aim to treat disease at the genetic level and have the added benefit of being more specific for their medicinal target." An example would be a genetic message that would arrest tumor growth.
A challenge has been that DNA and RNA drugs - pieces of genetic code that store information and instructions - cannot diffuse through the cell the way traditional small molecule drugs can. "We needed a vehicle to carry them into cells," said Reineke. One such vehicle has been engineered viruses. Reineke's group has been working on a more elegant solution. Their discovery is the topic of the PNAS article.
The scientists created novel polycations. A polycation is a polymer chain with positive charges, which is not too unusual. DNA itself is a polyanion, a polymer with negative charges. However, the Reineke Group's supramolecule has options. It contains chemistry (oligoethyleneamines) that binds and compacts nucleic acids - pieces of the DNA - into nanoparticles. It also incorporates a group of rare-earth elements known as lanthanides. The repackaged DNA is protected from damage as it travels into the cells and the lanthanides allow visualization of the delivery into cells.
"In our experiments, these delivery beacons provide the ability to track DNA delivery into living cells," said Reineke. "They provide the potential for tracking genetic therapies within the living body," she said.
At the nanometer or cellular scale, the researchers are able to track the polymers using sensitive microscopes, which capture the nanoparticle luminescence. At the sub-millimeter or tissue scale, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is used to see where the nanoparticles are going.
"This ability to track the movement and delivery of a gene-based drug provides an opportunity to understand the mechanism of delivery and monitor efficacy in real time, so that we can develop better materials for delivering genetic therapeutics and ultimately better treatments," Reineke said.
The research was published in the October 6, 2009 edition and the September 23 online edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), in the article "Polymer beacons for luminescence and magnetic resonance imaging of DNA delivery," by Joshua M. Bryson of Cincinnati, a recent student with the Macromolecules and Interfaces Institute (MII) at Virginia Tech, who received his Ph.D. in organic chemistry in August 2009 and is now principal scientist at Techulon Inc.; Katye M. Fichter, recent biochemistry graduate from the University of Cincinnati now a postdoctoral fellow at Oregon Health and Science University; Wen-Jang Chu, research assistant professor, and Jing-Huei Lee, associate professor, both of the University of Cincinnati Center for Imaging Research; Jing Li, a postdoctoral associate with MII; Louis A. Madsen, assistant professor of chemistry with MII; Patrick M. Mclendon of Cincinnati, a Ph.D. student in chemistry in Reineke's group, and Reineke. An abstract is available at www.pnas.org/content/early/2009/09/23/0904860106.abstract
The research was supported by Reineke's Alfred P. Sloan Research Fellowship and by the Camille Dreyfus Teacher-Scholar Awards Program.
Dr. Reineke has just been awarded the NIH Director's New Innovator Award (nihroadmap.nih.gov/newinnovator/index.asp). Learn more about her research at: www.reinekegroup.org
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Susan Trulove
540-231-5646
Copyright © Virginia Tech
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








