Home > Press > Acoustic tweezers can position tiny objects
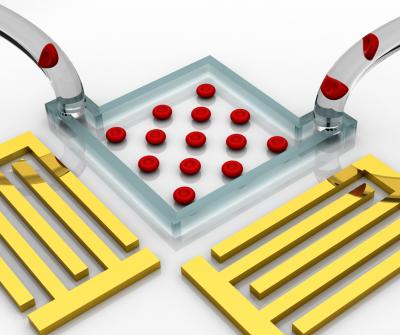 |
| "Acoustic tweezers" enable flexible on-chip manipulation and patterning of cells using standing surface acoustic waves. Credit: Tony Jun Huang, Jinjie Shi, Penn State |
Abstract:
Manipulating tiny objects like single cells or nanosized beads often requires relatively large, unwieldy equipment, but now a system that uses sound as a tiny tweezers can be small enough to place on a chip, according to Penn State engineers.
Acoustic tweezers can position tiny objects
University Park, PA | Posted on September 1st, 2009"Current methods for moving individual cells or tiny beads include such devices as optical tweezers, which require a lot of energy and could damage or even kill live cells," said Tony Jun Huang, assistant professor of engineering science and mechanics. "Acoustic tweezers are much smaller than optical tweezers and use 500,000 times less energy."
While optical tweezers are large and expensive, acoustic tweezers are smaller than a dime, small enough to fabricate on a chip using standard chip manufacturing techniques. They can also manipulate live cells without damaging or killing them.
Acoustic tweezers differ from eyebrow tweezers in that they position many tiny objects simultaneously and place them equidistant from each other in either parallel lines or on a grid. The grid configuration is probably the most useful for biological applications where researchers can place stem cells on a grid for testing or skin cells on a grid to grow new skin. This allows investigators to see how any type of cell grows.
"Acoustic tweezers are not just useful in biology," said Huang. "They can be used in physics, chemistry and materials science to create patterns of nanoparticles for coatings or to etch surfaces."
Acoustic tweezers work by setting up a standing surface acoustic wave. If two sound sources are placed opposite each other and each emits the same wavelength of sound, there will be a location where the opposing sounds cancel each other. This location can be considered a trough. Because sound waves have pressure, they can push very small objects, so a cell or nanoparticle will move with the sound wave until it reaches the trough where there is no longer movement. The particle or cell will stop and "fall" into the trough.
If the sound comes from two parallel sound sources facing each other, the troughs form a line or series of lines. If the sound sources are at right angles to each other, the troughs form an evenly spaced set of rows and columns like a checkerboard. Here too, the particles are pushed until they reach the location where the sound is no longer moving.
The acoustic tweezers are manufactured by fabricating an interdigital transducer onto a piezoelectric chip surface. These transducers are the source of the sound. Next, using standard photolithography, microchannels are fabricated in which a small amount of liquid with the cells or particles can move around freely. These microchannels were bonded to the chip to create the area for particle movement.
To test their device, the researchers, who include Jinjie Shi, Daniel Ahmed and Sz-Chin Steven Lin, graduate students, engineering science and mechanics; Xiaole Mao, graduate student in bioengineering, and Aitan Lawit, undergraduate in engineering science and mechanics, used Dragon Green fluorescent polystyrene beads about 1.9 micrometers in diameter. They then used cows red blood cells and the single cell bacteria E. coli to test the acoustic tweezers.
"The results verify the versatility of our technique as the two groups of cells differ significantly in both shape (spherical beads vs. rod-shaped E. coli) and size," the researchers reported in a recent issue of Lab on a Chip. They note that the patterning performance is independent of the particle's electrical, magnetic and optical properties.
"Most cells or particles patterned in a few seconds," said Huang. "The energy used is very low and the acoustic tweezers should not damage cells at all. Because they have different properties, the acoustic tweezers could also separate live from dead cells, or different types of particles."
Acoustic tweezers technology has significant advantages over existing technologies because of its versatility, miniaturization, power consumption and technical simplicity. Huang expects it to become a powerful tool for many applications such as tissue engineering, cell studies, and drug screening and discovery.
The National Science Foundation supported this work.
####
About Penn State
Penn State is a multi-campus public research university that improves the lives of the people of Pennsylvania, the nation, and the world through integrated, high-quality programs in teaching, research, and service.
Our instructional mission includes undergraduate, graduate, professional, and continuing and distance education informed by scholarship and research.
Our research, scholarship, and creative activities promote human and economic development through the expansion of knowledge and its applications in the natural and applied sciences, social sciences, arts, humanities, and professions. As Pennsylvania's land-grant university, we also hold a unique responsibility to provide access, outreach, and public service to support the citizens of the Commonwealth and beyond. We engage in collaborative activities with industrial, educational, and agricultural partners here and abroad to generate, disseminate, integrate, and apply knowledge.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
A'ndrea Elyse Messer
814-865-9481
Copyright © Penn State
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Chemistry
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Tools
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
![]() Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
![]() Physicists unlock the secret of elusive quantum negative entanglement entropy using simple classical hardware August 16th, 2024
Physicists unlock the secret of elusive quantum negative entanglement entropy using simple classical hardware August 16th, 2024
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








