Home > Press > Faculty Profile: Nina Markovic - Unraveling the Mysteries of Physics on the Nanoscale
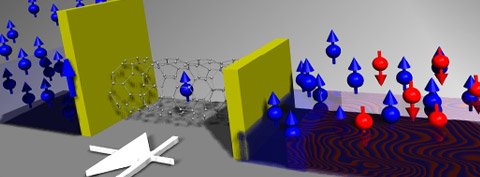 |
| Spin-diode with a nanotube quantum dot (QD) poised between a ferromagnetic (blue) and a non-ferromagnetic metal electrode (red and blue). Yellow walls represent contact barriers between the QD and the electrodes. Credit: Christopher Merchant/JHU |
Abstract:
Quantum dots (QD)—nanoscale particles that confine electrons and can emit and absorb light—have been studied in lasers, solar paneling, and biomedical therapeutics. Nina Markovic, affiliated faculty member of the Johns Hopkins Institute for NanoBioTechnology (INBT) and assistant professor of physics in the Krieger School of Arts and Sciences, believes this emerging technology will prove important in cancer therapies, energy transmission, and drug delivery.
Faculty Profile: Nina Markovic - Unraveling the Mysteries of Physics on the Nanoscale
Baltimore, MD | Posted on October 28th, 2008"Nanocrystal quantum dots are commercially available," Markovic says, "but we are developing a novel kind of quantum dots using carbon nanotubes."
Carbon nanotubes are long and narrow molecules that look like chicken wire made of carbon atoms. Their fascinating electronic, optical and mechanical properties have been extensively studied in the last ten years. Now that their basic properties are better understood, Markovic explains, the next step is to apply them to biomedical applications such as quantum dot therapeutics or diagnostics.
Recently, Markovic began collaborations with INBT affiliated faculty members Justin Hanes, professor in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and Jennifer Sample from the Applied Physics Laboratory. Together they have been investigating nanotube quantum dots for therapeutic purposes. Markovic and Sample have just been awarded a seed grant from INBT to develop this program.
Specifically, Markovic's group is working on ways to get their nanotube quantum dots to be frequency-specific. This means they will be able to release their contents on demand and be more selectively controlled—an important step in the specific time-release of drugs, and drug delivery regimes.
In addition, Markovic is interested in quantum computing and applying nanotube quantum dot technology to photovoltaic devices. Her group recently studied a film composed of carbon nanotubes and studied their photovoltaic currents in an innovative type of solar cell. Whereas semiconductors are typically used, her idea is to create a structurally different solar cell that may better transmit electrons from the photons it receives from the sun through the photovoltaic effect.
"If light can be more efficiently captured and converted into an electric current, it may revolutionize solar paneling and its use as an efficient renewable energy," Markovic says. [See reference.]
Markovic first became fascinated by quantum mechanics when she took a modern physics course as an undergraduate at the University of Zagreb, Croatia. She says she was drawn to its counterintuitive nature and its elegant mathematical language. After completing a post-doctoral fellowship at Harvard University in 2003, Markovic joined the Hopkins physics faculty. In 2004, she was selected as one of the Alfred P. Sloan Fellows. She received the distinguished National Science Foundation's Faculty Early Career Development Award in 2006, which gave her $500,000 over five years. Markovic enjoys the classroom and teaches thermodynamics and statistical physics. She particularly enjoys teaching the Frontiers of Physics course for non-science majors, which covers all aspects of physics from quantum physics to astrophysics.
To learn more about the Markovic Lab, physics-astronomy.jhu.edu/people/faculty/nina.html.
Reference:
"Effects of diffusion on photocurrent generation in single-walled carbon nanotube films," C. A. Merchant and N. Markovic, Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 243510 (2008).
Story by Jacob Koskimaki, INBT science writing intern and NanoBio IGERT fellow
####
About Institute for NanoBioTechnology
The Institute for NanoBioTechnology at Johns Hopkins University is revolutionizing health care by bringing together internationally renowned expertise in medicine, engineering, the sciences, and public health to create new knowledge and groundbreaking technologies.
INBT programs in research, education, outreach, and technology transfer are designed to foster the next wave of nanobiotechnology innovation.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
* Institute for NanoBioTechnology
214 Maryland Hall
3400 North Charles Street
Baltimore, MD 21218
* Email:
* Phone: (410) 516-3423
* Fax: (410) 516-2355
Copyright © Institute for NanoBioTechnology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum Dots/Rods
![]() A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
![]() IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
![]() Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
![]() NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








