Home > Press > IMEC reports method to extend lifetime of organic solar cells
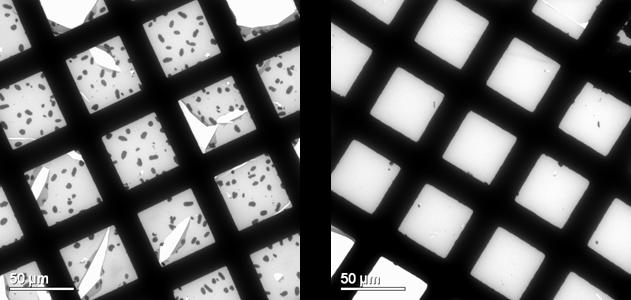 |
| Transmission Electron Microscopy results for polymer/PCBM 1:1 active layers after degradation at 100įC for 2 h, showing phase segregation for the Rieke P3HT polymer (left), but a stable morphology for the novel conjugated polymer (right) |
Abstract:
IMEC's associated laboratory IMOMEC, located on the campus of the Hasselt University, developed a method to stabilize the nanomorphology of organic solar cells resulting in a lifetime improvement of at least a factor 10. With these stabilized solar cells, efficiencies were achieved comparable to state-of-the-art organic solar cells. This breakthrough paves the way to commercial organic solar cells with an operational lifetime of over 5 years and efficiencies of over 10%.
IMEC reports method to extend lifetime of organic solar cells
Leuven, Belgium | Posted on October 14th, 2008The efficiency and operation of organic solar cells strongly depends on the nanomorphology of the active layer, i.e. on a stable mix of organic compounds that can trap the light's energy and transport it to an electric contact. IMEC already reported such cells based on P3HT:PCBM with efficiencies near 5%. But to date, the lifetime of these cells is far too short for commercial applications, for which 5 years is seen as a minimum. Under long term operation, all solar cells based on an intimate mixing of organic semiconductors deteriorate. This is due to segregation of the mixture whereby the compounds tend to separate into different phases and consequently reduce the efficient conversion of light into electricity. IMEC has shown before that this phase segregation is related to the mobility of the organic polymer and that fixation of the nanomorphology of the polymers could result in a prolonged operational lifetime.
IMEC/IMOMEC has now introduced a new method and new conjugated polymers to stabilize the nanomorphology of the active layer making it far more robust to phase segregation under prolonged operation. Experiments on bulk heterojunction organic solar cells based on this new material showed no degradation of the efficiency after more than 100 hours whereas reference cells degraded already after a few hours. This means that a lifetime improvement of at least a factor 10 can be obtained. And the cells achieved efficiencies near 4% which is comparable to state-of-the-art.
Future research targets further refinement of the method by optimizing the chemical structures of the conjugated polymers.
####
About IMEC
IMEC is a world-leading independent research center in nanoelectronics and nanotechnology. IMEC vzw is headquartered in Leuven, Belgium, has a sister company in the Netherlands, IMEC-NL, offices in the US, China and Taiwan, and representatives in Japan. Its staff of more than 1600 people includes more than 500 industrial residents and guest researchers. In 2007, its revenue (P&L) was EUR 244.5 million.
IMECís More Moore research aims at semiconductor scaling towards sub-32nm nodes. With its More than Moore research, IMEC looks into technologies for nomadic embedded systems, wireless autonomous transducer solutions, biomedical electronics, photovoltaics, organic electronics and GaN power electronics.
IMECís research bridges the gap between fundamental research at universities and technology development in industry. Its unique balance of processing and system know-how, intellectual property portfolio, state-of-the-art infrastructure and its strong network worldwide position IMEC as a key partner for shaping technologies for future systems.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Katrien Marent
Director of External Communications
T: +32 16 28 18 80
Mobile : +32 474 30 28 66
Copyright © IMEC
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








