Home > Press > Controlling Nanoparticle Size
Abstract:
New mechanism by which polymer materials used in nanocomposites control the growth of particles
Controlling Nanoparticle Size: Researchers Find New Mechanism Governing Particle Growth in Nanocomposites
September 01, 2005
Because the properties of nanoparticles depend so closely on their size, size distribution and morphology, techniques for controlling the growth of these tiny structures is of great interest to materials researchers today.
A research team from the Georgia Institute of Technology and Drexel University has discovered a surprising new mechanism by which polymer materials used in nanocomposites control the growth of particles. Reported on August 28th at the 230th national meeting of the American Chemical Society, the findings could provide a new tool for controlling the formation of nanoparticles.
Growing particles within the confinement of polymer-based structures is one technique commonly used for controlling nanoparticle growth. After formation of the particles, the polymer matrix can be removed – or the resulting nanocomposite used for a variety of applications.
In a series of experiments, the research team found a strong relationship between the chemical reactivity of the polymer and the size and shape of resulting nanoparticles.
“We have concentrated on the reactivity of the polymeric matrix and how that influences the growth of particles,” explained Rina Tannenbaum, an associate professor in Georgia Tech’s School of Materials Science and Engineering. “We found that in the melt the key parameter influencing particle size is actually the type of interaction with the polymer. The molecular weight of the polymer and the synthesis temperature are almost insignificant.”
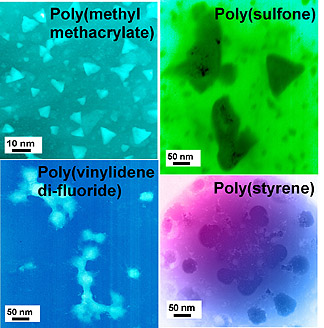
In a series of experiments, Tannenbaum and her collaborators created iron oxide nanoparticles within polymer films of different types, including polystyrene, poly(methyl methacrylate), bisphenol polycarbonate, poly(vinylidene di-fluouride) and polysulfone. The polymeric matrix was then decomposed using heat, leaving the particles to be characterized using transmission electron microscopy.
“These polymers spanned a variety of functional groups that differed in the strength and nature of their interactions with the iron oxide particles and in their position along with polymer chain,” Tannenbaum explained. “We found that the characteristic nanoparticle size decreased with the increasing affinity – the strength of the interaction – between the polymer and the iron oxide particles.”
Specifically, iron oxide particles formed in strongly interacting polymer media tended to be small (10-20 nanometers in diameter) and pyramid-shaped, while those formed in weakly-interacting media tended to be larger (40 to 60 nanometers in diameter) and spherical.
The researchers also found that the length of the polymer chain was only weakly related to the particle growth. “This means that for the same result, we can work in the melt with lower molecular-weight materials and have lower glass transitions,” Tannenbaum explained.
Based on the experimental results, Tannenbaum and Associate Professor Nily Dan of Drexel’s Department of Chemical Engineering charted the relationship between average particle size and the reactivity of the polymer interface. That information should help other scientists as they attempt to regulate the growth of nanoparticles using polymer reactivity.
Tannenbaum and Dan theorize that the polymer layer surrounding a nanoparticle while it grows favors an optimal interfacial curvature that sets the equilibrium particle characteristics. That may be related to the free energy of the adsorbed polymer layer.
While the researchers focused on iron oxide in this work, they believe the control mechanism should be broadly applicable to other particles and polymeric materials.
Next, the researchers plan to explore the influence of polymers in solution – a more complicated task involving more variables.
“In solution, the situation is much more complicated,” Tannenbaum said. “The polymer chains are on the loose, and face competition from the solvent. The chains will be reluctant to adsorb onto the surface of the particles, so we may end up with larger particles than in the melt. In solution, molecular weight of the polymer will have an impact.”
The work reported at the American Chemical Society meeting is part of a broader study of how nanoparticles interact with polymers – specifically, the interface between polymer chains and nanoparticles.
“The interface has important fundamental properties,” Tannenbaum noted. “When you look at nanocomposites, the interface is a very large component of the whole structure. You can’t look at a nanocomposite as having just two components – the interface is really a third.”
Beyond their use as a means for controlling nanoparticle size, nanocomposites may also have applications of their own. Their periodic structure, for instance, can be useful in optical and photonic applications.
The research has been sponsored by the National Science Foundation, Petroleum Research Fund of the American Chemical Society, U.S. Air Force Research Labs and Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA).
Tannenbaum, Dan and collaborators Melissa Zubris of Georgia Tech, Eugene Goldberg of the University of Florida, and Shimon Reich of the Weizmann Institute of Science earlier reported on the polymer-directed synthesis of nanoclusters in the journal Macromolecules.
John Toon
404-894-6986
john.toon@edi.gatech.edu
Fax (404-894-4545)
Jane Sanders
404-894-2214
jane.sanders@edi.gatech.edu
Technical Contact:
Rina Tannenbaum
404-385-1235
rina.tannenbaum@mse.gatech.edu
Copyright © Georgia Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||