Home > Press > Engineers find antioxidants improve nanoscale visualization of polymers
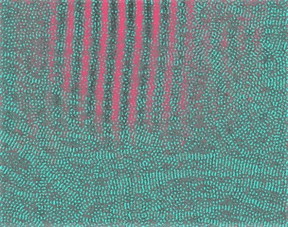 |
| Adding antioxidants can push the resolution limit of polymer electron microscopy to reveal a structure smaller in scale (blue) compared to the structure previously observed (pink) in this false-color image. CREDIT Brooke Kuei, Penn State |
Abstract:
Reactive molecules, such as free radicals, can be produced in the body after exposure to certain environments or substances and go on to cause cell damage. Antioxidants can minimize this damage by interacting with the radicals before they affect cells.
Engineers find antioxidants improve nanoscale visualization of polymers
University Park, PA | Posted on January 8th, 2021Led by Enrique Gomez, professor of chemical engineering and materials science and engineering, Penn State researchers have applied this concept to prevent imaging damage to conducting polymers that comprise soft electronic devices, such as organic solar cells, organic transistors, bioelectronic devices and flexible electronics. The researchers published their findings in Nature Communications today (Jan. 8).
According to Gomez, visualizing the structures of conducting polymers is crucial to further develop these materials and enable commercialization of soft electronic devices -- but the actual imaging can cause damage that limits what researchers can see and understand.
"It turns out antioxidants, like those you'd find in berries, aren't just good for you but are also good for polymer microscopy," Gomez said.
Polymers can only be imaged to a certain point with high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) because the bombardment of electrons used to form images breaks the sample apart.
The researchers examined this damage with the goal of identifying its fundamental cause. They found the HRTEM electron beam generated free radicals that degraded the sample's molecular structure. Introducing butylated hydroxytoluene, an antioxidant often used as a food additive, to the polymer sample prevented this damage and removed another restriction on imaging conditions -- temperature.
"Until now, the main strategy for minimizing polymer damage has been imaging at very low temperatures," said paper co-author Brooke Kuei, who earned her doctorate in materials science and engineering in the Penn State College of Earth and Mineral Sciences in August. "Our work demonstrates that the beam damage can be minimized with the addition of antioxidants at room temperature."
Although the researchers did not quantitatively test the resolution limits that resulted from this method, they were able to image the polymer at a resolution of 3.6 angstroms, an improvement from their previous resolution of 16 angstroms. For comparison, an angstrom is about one-millionth the breadth of a human hair.
Polymers are made up of molecular chains lying on top of each other. The previously imaged distance of 16 angstroms was the distance between chains, but imaging at 3.6 angstroms allowed researchers to visualize patterns of close contacts along the chains. For the electrically conductive polymer examined in this study, researchers could follow the direction along which electrons travel. According to Gomez, this allows them to better understand the conductive structures in polymers.
"The key to this advancement in polymer microscopy was understanding the fundamentals of how the damage occurs in these polymers," Gomez said. "This technological advance will hopefully help lead to the next generation of organic polymers."
###
The National Science Foundation and Kuei's graduate fellowship through the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science supported this work.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Megan Lakatos
814-865-5544
@penn_state
Copyright © Penn State
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Flexible Electronics
![]() Flexible electronics integrated with paper-thin structure for use in space January 17th, 2025
Flexible electronics integrated with paper-thin structure for use in space January 17th, 2025
![]() Beyond wires: Bubble technology powers next-generation electronics:New laser-based bubble printing technique creates ultra-flexible liquid metal circuits November 8th, 2024
Beyond wires: Bubble technology powers next-generation electronics:New laser-based bubble printing technique creates ultra-flexible liquid metal circuits November 8th, 2024
Organic Electronics
![]() Unveiling the power of hot carriers in plasmonic nanostructures August 16th, 2024
Unveiling the power of hot carriers in plasmonic nanostructures August 16th, 2024
![]() Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
![]() New organic molecule shatters phosphorescence efficiency records and paves way for rare metal-free applications July 5th, 2024
New organic molecule shatters phosphorescence efficiency records and paves way for rare metal-free applications July 5th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








