Home > Press > Moving diagnostics out of the lab and into your hand: Electrochemical sensor platform technology could enable portable, multiplexed, point-of-care diagnostics for a wide range of applications
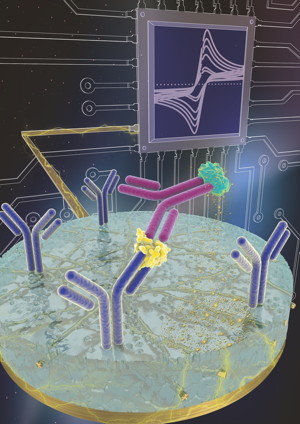 |
| Central to eRapid’s success is an antifouling coating on top of the electrode that is permeated by conductive components. When a target (yellow) binds to its probe (purple), it attracts a secondary probe (magenta) that initiates the precipitation of a compound onto the electrode, generating an electrical signal that reports the concentration of the target molecule. Credit: Wyss Institute at Harvard University |
Abstract:
Handheld electrochemical sensors are part of the daily routine for millions of people with diabetes around the globe who monitor their blood sugar levels with electric glucometers. While such sensors have revolutionized at-home medical testing for diabetics, they have not yet been successfully applied to diagnosing other conditions. Sensors like glucometers detect glucose in blood based on the activity of an enzyme, and there are only a limited number of enzymes that can be used to sense biomarkers of human disease. An alternative detection strategy based on binding events between antibodies and their molecular targets have been investigated to expand the use of electrochemical sensors for medicine, but these sensors fall victim to the rapid accumulation of "fouling" substances from biological fluids on their conductive surfaces, which deactivate them. Existing antifouling coatings are difficult to mass-manufacture, suffer from quality and consistency issues, and are not very effective.
Moving diagnostics out of the lab and into your hand: Electrochemical sensor platform technology could enable portable, multiplexed, point-of-care diagnostics for a wide range of applications
Cambridge, MA | Posted on November 11th, 2019Now, a new diagnostic platform technology developed by researchers at the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University known as "eRapid" enables the creation of low-cost, handheld electrochemical devices that can simultaneously detect a broad range of biomarkers with high sensitivity and selectivity in complex biological fluids, using as little as a single drop of blood. The technology is described in the newest issue of Nature Nanotechnology.
"As long as an antibody exists for a given target molecule, eRapid can detect it," said co-author Pawan Jolly, Ph.D., a Senior Research Scientist at the Wyss Institute. "By solving the biofouling problem with a simple yet robust design, we are now able to easily mass-produce biochemical sensors for a wide variety of applications at low-cost."
The challenge in developing the antifouling coating was to prevent accumulation of off-target substances on the sensor's metal electrodes while still maintaining their conductivity to allow sensing of the target. After experimenting with a variety of recipes, the research team developed a simple, porous, 3D matrix consisting of bovine serum albumin (BSA) crosslinked with glutaraldehyde and supported by a network of conducting nanomaterials, such as gold nanowires or carbon nanotubes. The small pore size of the BSA matrix size-excludes proteins found in blood and plasma, and the BSA's weak negative charge prevents the strong adhesion of positively charged biomolecules onto the sensor.
When the researchers tested their nanomaterial-coated sensors in human blood serum and plasma, they retained more than 90% of their ability to detect signal even after being stored for one month in those biofluids, whereas sensors coated with best previously published anti-fouling coatings lost significant signal sensitivity when incubated for one hour, and were completely inactivated after one day.
To functionalize the coated sensors, the researchers attached antibodies to the surface of the nanomaterial coating on top of the electrode, and used a "sandwich assay" to convert the antibody binding event into a chemical signal that precipitates onto the electrode surface, thereby generating an electric signal. The magnitude of the electrical signal directly correlates to the amount of the precipitate produced, and thus to the number of target molecules bound to the antibodies, allowing the concentration of the target to be measured.
The team demonstrated the commercial utility of this approach by creating a multiplexed sensor with three separate electrodes, each coated with the BSA/gold nanowire matrix and a layer of antibodies against a specific clinically relevant target molecule: interleukin 6 (IL6), insulin, or glucagon. When they incubated the sensor with the respective target molecules in undiluted human plasma, they observed excellent electrical signals with picogram-per-mL sensitivity. Conversely, electrodes coated with a published "PEG-SAM" anti-fouling coating failed to produce distinct signals, indicating that they had been irreversibly fouled by off-target molecules in human plasma samples. In addition, the BSA/gold-nanowire-coated sensors can be washed and reused multiple times with minimal signal loss, allowing serial monitoring of biomarkers easily and at low cost.
Since then, the Wyss team has been able to detect more than a dozen different biomarkers ranging from 100 Da to 150,000 Da in size with eRapid, and they are continuing to experiment with conductive nanomaterials to optimize the electrode coating and the system's performance, as well as reduce the cost even further. They are actively exploring commercialization options for eRapid in the handheld point-of-care diagnostics space, but also hope to extend the coating and sensor technology platform to other targets and contexts, including in-hospital diagnostics, environmental toxin sensing, small molecule detection, and implantable medical devices.
Interestingly, the team - led by the Wyss Institute's Founding Director Donald Ingber, M.D., Ph.D. - did not originally set out with this goal in mind. This work began because they needed to simultaneously detect multiple biomolecules produced by various types of tissue cells growing within human Organs-on-Chips to non-invasively assess their function and inflammatory status over time. The tiny volume of liquid outflows from the chips' channels necessitated highly sensitive sensors that could also be multiplexed, which led to the creation of the current technology.
"eRapid emerged from pursuing one innovation that led to another that has the potential to transform medical diagnostics. Hopefully, this simple technology will enable great advances in our ability to develop handheld diagnostic devices that can be used at home, as well as in pharmacies, ambulances, doctor's offices, and emergency departments in the near future," said Ingber who is also the Judah Folkman Professor of Vascular Biology at Harvard Medical School and the Vascular Biology Program at Boston Children's Hospital, and Professor of Bioengineering at Harvard's John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences.
###
Additional authors of the paper include former Wyss members Jonathan Sabaté del Río, Ph.D., who is currently a Postdoctoral Fellow at the Institute for Basic Science in Korea and Olivier Henry, Ph.D., who is currently a Program Manager at Imec in Belgium. This research was supported by the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering, the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency, the Institute for Basic Science, the KeepSmilin4Abbie Foundation, and the National Science Foundation.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Lindsay Brownell
617-432-8266
@wyssinstitute
Copyright © Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Lab-on-a-chip
![]() Micro-scale opto-thermo-mechanical actuation in the dry adhesive regime Peer-Reviewed Publication September 24th, 2021
Micro-scale opto-thermo-mechanical actuation in the dry adhesive regime Peer-Reviewed Publication September 24th, 2021
![]() Silicon-graphene hybrid plasmonic waveguide photodetectors beyond 1.55 μm March 13th, 2020
Silicon-graphene hybrid plasmonic waveguide photodetectors beyond 1.55 μm March 13th, 2020
![]() Trapping and moving tiny particles using light September 24th, 2019
Trapping and moving tiny particles using light September 24th, 2019
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Sensors
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
![]() Physicists unlock the secret of elusive quantum negative entanglement entropy using simple classical hardware August 16th, 2024
Physicists unlock the secret of elusive quantum negative entanglement entropy using simple classical hardware August 16th, 2024
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








