Home > Press > 2D borophene gets a closer look: Rice, Northwestern find new ways to image, characterize unique material
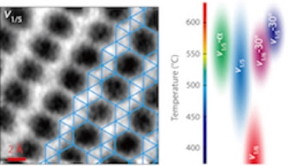 |
| Scientists at Rice and Northwestern universities have developed a technique to get images of two-dimensional borophene and match them with models. Polymorphic borophene shows promise for electronic, thermal, optical and other applications. The researchers also created a phase diagram, at right, with details about borophene polymorphs observed to date. (Credit: Xiaolong Liu/Northwestern University) |
Abstract:
Graphene can come from graphite. But borophene? There's no such thing as borite.
2D borophene gets a closer look: Rice, Northwestern find new ways to image, characterize unique material
Houston, TX | Posted on April 11th, 2019Unlike its carbon cousin, two-dimensional borophene can't be reduced from a larger natural form. Bulk boron is usually only found in combination with other elements, and is certainly not layered, so borophene has to be made from the atoms up. Even then, the borophene you get may not be what you need.
For that reason, researchers at Rice and Northwestern universities have developed a method to view 2D borophene crystals, which can have many lattice configurations -- called polymorphs -- that in turn determine their characteristics.
Knowing how to achieve specific polymorphs could help manufacturers incorporate borophene with desirable electronic, thermal, optical and other physical properties into products.
Boris Yakobson, a materials physicist at Rice's Brown School of Engineering, and materials scientist Mark Hersam of Northwestern led a team that not only discovered how to see the nanoscale structures of borophene lattices but also built theoretical models that helped characterize the crystalline forms.
Their results are published in Nature Communications.
Borophene remains hard to make in even small quantities. If and when it can be scaled up, manufacturers will likely want to fine-tune it for applications. What the Rice and Northwestern teams learned will help in that regard.
Graphene takes a single form – an array of hexagons, like chicken wire – but perfect borophene is a grid of triangles. However, borophene is a polymorph, a material that can have more than one crystal structure. Vacancies that leave patterns of "hollow hexagons" in a borophene lattice determine its physical and electrical properties.
Yakobson said there could theoretically be more than 1,000 forms of borophene, each with unique characteristics.
"It has many possible patterns and networks of atoms being connected in the lattice," he said.
The project started at Hersam's Northwestern lab, where researchers modified the blunt tip of an atomic force microscope with a sharp tip of carbon and oxygen atoms. That gave them the ability to scan a flake of borophene to sense electrons that correspond to covalent bonds between boron atoms. They used a similarly modified scanning tunneling microscope to find hollow hexagons where a boron atom had gone missing.
Scanning flakes grown on silver substrates under various temperatures via molecular-beam epitaxy showed them a range of crystal structures, as the changing growth conditions altered the lattice.
“Modern microscopy is very sophisticated, but the result is, unfortunately, that the image you get is generally difficult to interpret," Yakobson said. "That is, it's hard to say an image corresponds to a particular atomic lattice. It's far from obvious, but that's where theory and simulations come in."
Yakobson's team used first-principle simulations to determine why borophene took on particular structures based on calculating the interacting energies of both boron and substrate atoms. Their models matched many of the borophene images produced at Northwestern.
"We learned from the simulations that the degree of charge transfer from the metal substrate into borophene is important," he said. "How much of this is happening, from nothing to a lot, can make a difference."
The researchers confirmed through their analysis that borophene is also not an epitaxial film. In other words, the atomic arrangement of the substrate doesn't dictate the arrangement or rotational angle of borophene.
The team produced a phase diagram that lays out how borophene is likely to form under certain temperatures and on a variety of substrates, and noted their microscopy advances will be valuable for finding the atomic structures of emerging 2D materials.
Looking to the future, Hersam said, "The development of methods to characterize and control the atomic structure of borophene is an important step toward realizing the many proposed applications of this material, which range from flexible electronics to emerging topics in quantum information sciences."
Xiaolong Liu of Northwestern and Luqing Wang of Rice are lead authors of the paper. Co-authors are Shaowei Li and Matthew Rahn of Northwestern. Yakobson is the Karl F. Hasselmann Professor of Materials Science and NanoEngineering and a professor of chemistry at Rice. Hersam is the Walter P. Murphy Professor of Materials Science and Engineering at Northwestern.
The Office of Naval Research, the National Science Foundation, the Department of Energy Office of Science and the Northwestern University International Institute for Nanotechnology supported the research.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation’s top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,962 undergraduates and 3,027 graduate students, Rice’s undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is just under 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for lots of race/class interaction and No. 2 for quality of life by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger’s Personal Finance.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Gold soaks up boron, spits out borophene:
Gold soaks up boron, spits out borophene:
![]() George R. Brown School of Engineering:
George R. Brown School of Engineering:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
2 Dimensional Materials
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Flexible Electronics
![]() Flexible electronics integrated with paper-thin structure for use in space January 17th, 2025
Flexible electronics integrated with paper-thin structure for use in space January 17th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
![]() Physicists unlock the secret of elusive quantum negative entanglement entropy using simple classical hardware August 16th, 2024
Physicists unlock the secret of elusive quantum negative entanglement entropy using simple classical hardware August 16th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
Quantum nanoscience
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








