Home > Press > Nuclear radiation detecting device could lead to new homeland security tool: New device can detect gamma rays and identify radioactive isotopes
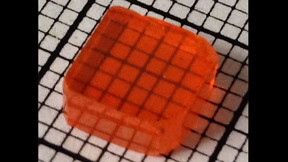 |
| A sample of cesium lead bromide, a new material that makes nuclear radiation detection cheaper and more accessible. |
Abstract:
It has been more than 30 years since a material with this performance has been developed
Material is inexpensive to produce, an advantage over material currently used
Other applications include biomedical imaging, astronomy and spectroscopy
Nuclear radiation detecting device could lead to new homeland security tool: New device can detect gamma rays and identify radioactive isotopes
Evanston, IL | Posted on April 25th, 2018 A Northwestern University and Argonne National Laboratory research team has developed an exceptional next-generation material for nuclear radiation detection that could provide a significantly less expensive alternative to the detectors now in commercial use.
Specifically, the high-performance material is used in a device that can detect gamma rays, weak signals given off by nuclear materials, and can easily identify individual radioactive isotopes. It has been more than 30 years since a material with this performance was developed, with the new material having the advantage of inexpensive production.
Potential uses for the new device include more widespread detectors -- including handheld -- for nuclear weapons and materials as well as applications in biomedical imaging, astronomy and spectroscopy.
“Governments of the world want a quick, low-cost way to detect gamma rays and nuclear radiation to fight terrorist activities, such as smuggling and dirty bombs, and the proliferation of nuclear materials,” said Northwestern’s Mercouri G. Kanatzidis, the corresponding author of the paper. “This has been a very difficult problem for scientists to solve. Now we have an exciting new semiconductor device that is inexpensive to make and works well at room temperature.”
Kanatzidis is a Charles E. and Emma H. Morrison Professor of Chemistry in the Weinberg College of Arts and Sciences. He has a joint appointment with Argonne.
The research was published this week in the journal Nature Communications.
In 2013, Argonne published a scientific study noting the promise of cesium lead bromide in the form of perovskite crystals for high-energy radiation detection. Since then, researchers led by Kanatzidis, Duck Young Chung of Argonne and Constantinos Stoumpos of Northwestern have worked to purify and improve the material.
The breakthrough came when Yihui He, a postdoctoral fellow in Kanatzidis’ group and the paper’s first author, took the improved material and reconfigured the semiconductor device. Instead of using the same electrode on either side of the crystal, he used two different electrodes. With this asymmetrical design, the device only conducts electricity when gamma rays are present.
The researchers compared the performance of their new cesium lead bromide detector to the conventional cadmium zinc telluride (CZT) detector and found it performed just as well in detecting gamma rays with high resolution from cobalt-57.
“We achieved the same performance in two years of research and development as others did in 20 years with cadmium zinc telluride, the expensive material that is currently used,” Kanatzidis said.
It is important to know what the gamma-ray emitting material is, Kanatzidis stressed, because some materials are legal and some are illegal. Each radioactive isotope possesses its own “fingerprint”: a different decay behavior and a unique characteristic gamma-ray emission spectrum. The new cesium lead bromide detector can detect these fingerprints.
In the study, the researchers found the detector successfully identified radioactive isotopes americium-241, cobalt-57, cesium-137 and sodium-22. The researchers also produced larger crystal samples to demonstrate the material can be scaled up.
The Department of Energy, National Nuclear Security Administration, Office of Defense Nuclear Nonproliferation Research and Development (contract No. DE-AC02-06CH11357, Argonne National Laboratory) and the Department of Homeland Security ARI program (grant 2014-DN-077-ARI086-01) supported the research.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Megan Fellman
847-491-3115
Copyright © Northwestern University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Law enforcement/Anti-Counterfeiting/Security/Loss prevention
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() New chip ramps up AI computing efficiency August 19th, 2022
New chip ramps up AI computing efficiency August 19th, 2022
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Homeland Security
![]() The picture of health: Virginia Tech researchers enhance bioimaging and sensing with quantum photonics June 30th, 2023
The picture of health: Virginia Tech researchers enhance bioimaging and sensing with quantum photonics June 30th, 2023
![]() Sensors developed at URI can identify threats at the molecular level: More sensitive than a dog's nose and the sensors don't get tired May 21st, 2021
Sensors developed at URI can identify threats at the molecular level: More sensitive than a dog's nose and the sensors don't get tired May 21st, 2021
![]() Highly sensitive dopamine detector uses 2D materials August 7th, 2020
Highly sensitive dopamine detector uses 2D materials August 7th, 2020
Military
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








