Home > Press > A new way to mix oil and water: Condensation-based method developed at MIT could create stable nanoscale emulsions
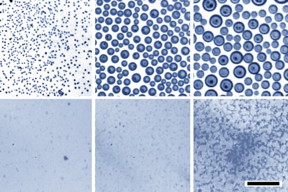 |
| Optical images demonstrate that when water droplets condense on an oil bath, the droplets rapidly coalesce to become larger and larger (top row of images, at 10-minute intervals). Under identical conditions but with a soap-like surfactant added (bottom row), the tiny droplets are much more stable and remain small. Courtesy of the researchers |
Abstract:
The reluctance of oil and water to mix together and stay that way is so well-known that it has become a cliché for describing any two things that do not go together well. Now, a new finding from researchers at MIT might turn that expression on its head, providing a way to get the two substances to mix and remain stable for long periods — no shaking required. The process may find applications in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and processed foods, among other areas.
A new way to mix oil and water: Condensation-based method developed at MIT could create stable nanoscale emulsions
Cambridge, MA | Posted on November 8th, 2017The new process involves cooling a bath of oil containing a small amount of a surfactant (a soap-like substance), and then letting water vapor from the surrounding air condense onto the oil surface. Experiments have shown that this can produce tiny, uniform water droplets on the surface that then sink into the oil, and their size can be controlled by adjusting the proportion of surfactant. The findings, by MIT graduate student Ingrid Guha, former postdoc Sushant Anand, and associate professor Kripa Varanasi, are reported in the journal Nature Communications.
As anyone who has ever used salad dressing knows, no matter how vigorously the mixture gets shaken, the oil and the vinegar (a water-based solution) will separate within minutes. But for many uses, including new drug-delivery systems and food-processing methods, it’s important to be able to get oil in water (or water in oil) to form tiny droplets — only a few hundred nanometers across, too small to see with the naked eye — and to have them stay tiny rather than coalescing into larger droplets and eventually separating from the other liquid.
Typically, in industrial processes these emulsions are made by either mechanically shaking the mix or using sound waves to set up intense vibrations within the liquid, a process called sonicating. But both of these processes “require a lot of energy,” Varanasi says, “and the finer the drops, the more energy it takes.” By contrast, “our approach is very energy inexpensive,” he adds.
“The key to overcoming that separation is to have really small, nanoscale droplets,” Guha explains. “When the drops are small, gravity can’t overcome them,” and they can remain suspended indefinitely.
For the new process, the team set up a reservoir of oil with an added surfactant that can bind to both oil and water molecules. They placed this inside a chamber with very humid air and then cooled the oil. Like a glass of cold water on a hot summer day, the colder surface causes the water vapor to precipitate. The condensing water then forms droplets at the surface that spread through the oil-surfactant mixture, and the sizes of these droplets are quite uniform, the team found. “If you get the chemistry just right, you can get just the right dispersion,” Guha says. By adjusting the proportion of surfactant in the oil, the droplet sizes can be well-controlled.
In the experiments, the team produced nanoscale emulsions that remained stable over periods of several months, compared to the few minutes that it takes for the same mixture of oil and water to separate without the added surfactant. “The droplets stay so small that they’re hard to see even under a microscope,” Guha says.
Unlike the shaking or sonicating methods, which take the large, separate masses of oil and water and gradually get them to break down into smaller drops — a “top down” approach — the condensation method starts off right away with the tiny droplets condensing out from the vapor, which the researchers call a bottom-up approach. “By cloaking the freshly condensed nanoscale water droplets with oil, we are taking advantage of the inherent nature of phase-change and spreading phenomena,” Varanasi says.
“Our bottom-up approach of creating nanoscale emulsions is highly scalable owing to the simplicity of the process,” Anand says. “We have uncovered many new phenomena during this work. We have found how the presence of surfactant can change the oil and water interactions under such conditions, promoting oil spreading on water droplets and stabilizing them at the nanoscale.”
The team says that the approach should work with a variety of oils and surfactants, and now that the process has been identified, their findings “provide a kind of design guideline for someone to use” for a particular kind of application, Varanasi says.
“It’s such an important thing,” he says, because “foods and pharmaceuticals always have an expiration date,” and often that has to do with the instability of the emulsions in them. The experiments used a particular surfactant that is widely used, but many other varieties are available, including some that are approved for food-grade products.
In addition, Guha says, “we envision that you could use multiple liquids and make much more complex emulsions.” And besides being used in food, cosmetics, and drugs, the method could have other applications, such as in the oil and gas industry, where fluids such as the drilling “muds” sent down wells are also emulsions, Varanasi says.
The work was supported by the MIT Energy Initiative, the National Science Foundation, and a Society in Science fellowship. Anand, the co-author who was a postdoc at MIT, is now an assistant professor at the University of Illinois.
###
Written by David L. Chandler, MIT News Office
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Karl-Lydie Jean-Baptiste
MIT News Office
617-253-1682
Copyright © Massachusetts Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Videos/Movies
![]() New X-ray imaging technique to study the transient phases of quantum materials December 29th, 2022
New X-ray imaging technique to study the transient phases of quantum materials December 29th, 2022
![]() Solvent study solves solar cell durability puzzle: Rice-led project could make perovskite cells ready for prime time September 23rd, 2022
Solvent study solves solar cell durability puzzle: Rice-led project could make perovskite cells ready for prime time September 23rd, 2022
![]() Scientists prepare for the world’s smallest race: Nanocar Race II March 18th, 2022
Scientists prepare for the world’s smallest race: Nanocar Race II March 18th, 2022
![]() Visualizing the invisible: New fluorescent DNA label reveals nanoscopic cancer features March 4th, 2022
Visualizing the invisible: New fluorescent DNA label reveals nanoscopic cancer features March 4th, 2022
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Food/Agriculture/Supplements
![]() Silver nanoparticles: guaranteeing antimicrobial safe-tea November 17th, 2023
Silver nanoparticles: guaranteeing antimicrobial safe-tea November 17th, 2023
![]() Night-time radiative warming using the atmosphere November 17th, 2023
Night-time radiative warming using the atmosphere November 17th, 2023
![]() DGIST and New Life Group launched a research project on "Functional beauty and health products using the latest nanotechnology" May 12th, 2023
DGIST and New Life Group launched a research project on "Functional beauty and health products using the latest nanotechnology" May 12th, 2023
Water
![]() Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Industrial
![]() Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
![]() Nanotubes: a promising solution for advanced rubber cables with 60% less conductive filler June 1st, 2022
Nanotubes: a promising solution for advanced rubber cables with 60% less conductive filler June 1st, 2022
![]() Protective equipment with graphene nanotubes meets the strictest ESD safety standards March 25th, 2022
Protective equipment with graphene nanotubes meets the strictest ESD safety standards March 25th, 2022
![]() OCSiAl receives the green light for Luxembourg graphene nanotube facility project to power the next generation of electric vehicles in Europe March 4th, 2022
OCSiAl receives the green light for Luxembourg graphene nanotube facility project to power the next generation of electric vehicles in Europe March 4th, 2022
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








