Home > Press > Regulation of two-dimensional nanomaterials: New driving force for lithium-ion batteries
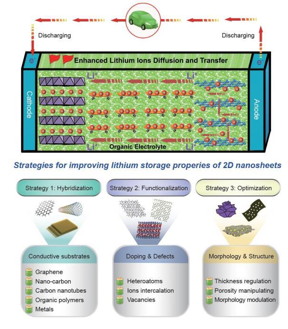 |
| Strategies for improving the lithium storage properties of 2D nanosheets. CREDIT ©Science China Press |
Abstract:
Li-ion batteries (LIBs) are attractive as the major energy storage devices due to their higher specific energy density, lower self-discharge, and lower memory effect. Among the components of batteries, electrode materials play a key role in enhancing electrochemical properties. Thus, the development of advanced electrode materials for high-performance LIBs has been the major objective in the related research fields.
Regulation of two-dimensional nanomaterials: New driving force for lithium-ion batteries
Beijing, China | Posted on July 26th, 2017Two-dimensional (2D) nanomaterials, including graphene, transition metal oxide (TMO) nanosheets, transition metal dichalcogenide (TMD) nanosheets, etc., are composed of one or several monolayers of atoms (or unit cells). They have been paid much attention in recent years, due to their outstanding physical and chemical properties in contrast to their bulk counterparts. The integration of 2D nanomaterials with energy storage devices could provide promising opportunities to overcome the major challenges driven by ever-growing global energy demands. Unfortunately, the direct use of these sheet-like materials has met with numerous challenges, such as serious self-agglomerating tendency, relatively low conductivity and the obvious volume changes over repeated charging-discharging cycles.
In a new review paper published in National Science Review, scientists from Australia at Queensland University of Technology and University of Wollongong summarized recent progress on the strategies for enhancing the lithium storage performance of 2D nanomaterials. These strategies for manipulating the structures and properties are expected to meet the major challenges for advanced nanomaterials in energy storage applications. Co-authors Jun Mei, Yuanwen Zhang, Ting Liao, Ziqi Sun and Shi Xue Dou classified these strategies into three primary strategies, including hybridization with conductive materials, surface/edge functionalization, and structural optimization.
"The strategy of hybridization is the most common and widely studied one for TMOs/TMDs-based nanocomposites, in which some conductive nanostructures, e.g. nano-carbon, carbon nanotubes (CNTs), graphene, organic polymers, metallic nanoparticles, etc., are introduced to hybridize with TMO/TMD nanosheets to improve the overall conductivity and accommodate the volume expansion of metal oxide or sulfide nanomaterials during the repeated charging/discharging cycles." they state.
"The second strategy is edge/surface functionalization, which can be achieved by atom/ion doping or defect engineering at the edges or on the surfaces of the 2D nanomaterials. The implantation of heteroatoms or ions into 2D nanomaterials helps to modulate the electronic structure, the surface chemical reactivity, or the interlayer spacing of the 2D nanomaterials, and further enhances the lithium ions storage capacity," they add. "The third strategy of structure optimization is often realized by controlling some structural parameters during fabrication, such as thickness, size, pores, or surface morphology, which have significant impacts on the structure-dependent properties and the electrochemical performance, and are beneficial for alleviating the inevitable self-restacking and exposing more active sites."
The scientists believe "these effective strategies for improving the lithium storage of 2D nanomaterials will be good reference points for scientists and researchers in the related fields of materials, chemistry, and nanotechnology, who are looking forward to developing superior next-generation rechargeable batteries".
####
About Science China Press
The National Science Review is the first comprehensive scholarly journal released in English in China that is aimed at linking the country's rapidly advancing community of scientists with the global frontiers of science and technology. The journal also aims to shine a worldwide spotlight on scientific research advances across China.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Ziqi Sun
Copyright © Science China Press
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() See the article: Jun Mei, Yuanwen Zhang, Ting Liao, Ziqi Sun and Shi Xue Dou
See the article: Jun Mei, Yuanwen Zhang, Ting Liao, Ziqi Sun and Shi Xue Dou
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
2 Dimensional Materials
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings
![]() Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
![]() Detection of bacteria and viruses with fluorescent nanotubes July 21st, 2023
Detection of bacteria and viruses with fluorescent nanotubes July 21st, 2023
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








