Home > Press > New method for making green LEDs enhances their efficiency and brightness
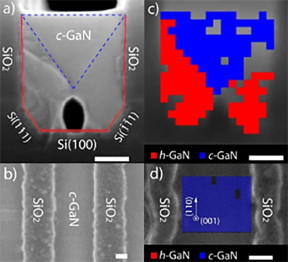 |
| A new method of cubic phase synthesis: Hexagonal-to-cubic phase transformation. The scale bars represent 100 nm in all images. (a) Cross sectional and (b) Top-view SEM images of cubic GaN grown on U-grooved Si(100). (c) Cross sectional and (d) Top-view EBSD images of cubic GaN grown on U-grooved Si(100), showing cubic GaN in blue, and hexagonal GaN in red. CREDIT: University of Illinois |
Abstract:
Researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign have developed a new method for making brighter and more efficient green light-emitting diodes (LEDs). Using an industry-standard semiconductor growth technique, they have created gallium nitride (GaN) cubic crystals grown on a silicon substrate that are capable of producing powerful green light for advanced solid-state lighting.
New method for making green LEDs enhances their efficiency and brightness
Urbana, IL | Posted on July 30th, 2016"This work is very revolutionary as it paves the way for novel green wavelength emitters that can target advanced solid-state lighting on a scalable CMOS-silicon platform by exploiting the new material, cubic gallium nitride," said Can Bayram, an assistant professor of electrical and computer engineering at Illinois who first began investigating this material while at IBM T.J. Watson Research Center several years ago.
"The union of solid-state lighting with sensing (e.g. detection) and networking (e.g. communication) to enable smart (i.e. responsive and adaptive) visible lighting, is further poised to revolutionize how we utilize light. And CMOS-compatible LEDs can facilitate fast, efficient, low-power, and multi-functional technology solutions with less of a footprint and at an ever more affordable device price point for these applications."
Typically, GaN forms in one of two crystal structures: hexagonal or cubic. Hexagonal GaN is thermodynamically stable and is by far the more conventional form of the semiconductor. However, hexagonal GaN is prone to a phenomenon known as polarization, where an internal electric field separates the negatively charged electrons and positively charged holes, preventing them from combining, which, in turn, diminishes the light output efficiency.
Until now, the only way researchers were able to make cubic GaN was to use molecular beam epitaxy, a very expensive and slow crystal growth method when compared to the widely used metal-organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) method that Bayram used.
Bayram and his graduate student Richard Liu made the cubic GaN by using lithography and isotropic etching to create a U-shaped groove on Si (100). This non-conducting layer essentially served as a boundary that shapes the hexagonal material into cubic form.
"Our cubic GaN does not have an internal electric field that separates the charge carriers--the holes and electrons," explained Liu. "So, they can overlap and when that happens, the electrons and holes combine faster to produce light."
Ultimately, Bayram and Liu believe their cubic GaN method may lead to LEDs free from the "droop" phenomenon that has plagued the LED industry for years. For green, blue, or ultra-violet LEDs, their light-emission efficiency declines as more current is injected, which is characterized as "droop."
"Our work suggests polarization plays an important role in the droop, pushing the electrons and holes away from each other, particularly under low-injection current densities," said Liu, who was the first author of the paper, ""Maximizing Cubic Phase Gallium Nitride Surface Coverage on Nano-patterned Silicon (100)", appearing Applied Physics Letters.
Having better performing green LEDs will open up new avenues for LEDs in general solid-state lighting. For example, these LEDs will provide energy savings by generating white light through a color mixing approach. Other advanced applications include ultra-parallel LED connectivity through phosphor-free green LEDs, underwater communications, and biotechnology such as optogenetics and migraine treatment.
Enhanced green LEDs aren't the only application for Bayram's cubic GaN, which could someday replace silicon to make power electronic devices found in laptop power adapters and electronic substations, and it could replace mercury lamps to make ultra-violet LEDs that disinfect water.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Can Bayram
217-300-0978
Copyright © University of Illinois College of Engineering
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() Light guide plate based on perovskite nanocomposites November 3rd, 2023
Light guide plate based on perovskite nanocomposites November 3rd, 2023
![]() Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
![]() Novel design perovskite electrochemical cell for light-emission and light-detection May 12th, 2023
Novel design perovskite electrochemical cell for light-emission and light-detection May 12th, 2023
![]() A universal HCl-assistant powder-to-powder strategy for preparing lead-free perovskites March 24th, 2023
A universal HCl-assistant powder-to-powder strategy for preparing lead-free perovskites March 24th, 2023
Hardware
![]() The present and future of computing get a boost from new research July 21st, 2023
The present and future of computing get a boost from new research July 21st, 2023
![]() A Carbon Nanotube Microprocessor Mature Enough to Say Hello: Three new breakthroughs make commercial nanotube processors possible March 2nd, 2020
A Carbon Nanotube Microprocessor Mature Enough to Say Hello: Three new breakthroughs make commercial nanotube processors possible March 2nd, 2020
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Water
![]() Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








