Home > Press > Attosecond physics: Mapping electromagnetic waveforms
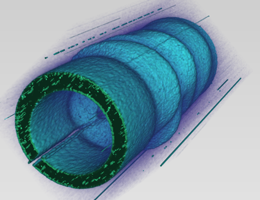 |
| A three-dimensional depiction of the spatial variation of the optical electromagnetic field around a microantenna following excitation with terahertz pulse. The optical field is mapped with the aid of electron pulses. Illustration: Peter Baum |
Abstract:
Munich physicists have developed a novel electron microscope that can visualize electromagnetic fields oscillating at frequencies of billions of cycles per second.
Attosecond physics: Mapping electromagnetic waveforms
Munich, Germany | Posted on July 25th, 2016Temporally varying electromagnetic fields are the driving force behind the whole of electronics. Their polarities can change at mind-bogglingly fast rates, and it is difficult to capture them in action. These fields control the flow of electrons in components such as 'field-effect' transistors, and are ultimately responsible for the manipulation, flow and storage of data in our computers and smartphones. However, a better understanding of the dynamics of field variation in electronic components, such as transistors, is indispensable for future advances in electronics. Researchers in the Laboratory for Attosecond Physics, jointly run by LMU and the Max Planck Institute for Quantum Optics (MPQ), have now taken an important step towards this goal - by building an electron microscope that can image high-frequency electromagnetic fields and trace their ultrafast dynamics.
This instrument makes use of ultrashort pulses of laser light, each of which lasts for a few femtoseconds (a femtosecond equals one millionth of a billionth (10-15) of a second). These laser pulses are used to generate bunches of electrons made up of very few particles, which are then temporally compressed by the action of terahertz (1012 Hz) near-infrared radiation. The LMU and MPQ physicists who belong to the research group in Ultrafast Electron Imaging first described this strategy earlier this year in the journal Science, and demonstrated that it can generate electron pulses that are shorter than a half-cycle of the optical field.
The researchers now show that these ultrashort electron pulses can be used to map high-frequency electromagnetic fields. In the experiment, the pulses are directed onto a microantenna that has just interacted with a precisely timed burst of terahertz radiation. The light pulse excites surface electrons in the antenna, thus creating an oscillating optical (electromagnetic) field in the immediate vicinity (the so-called near field) of the target. When the electron pulses come under the influence of the induced electromagnetic field around the antenna, they are scattered, and the pattern of their deflection is recorded. On the basis of the dispersion of the deflected electrons, the researchers can reconstruct the spatial distribution, temporal variation, orientation and polarization of the light emitted by the microantenna.
"In order to visualize electromagnetic fields oscillating at optical frequencies, two important conditions must be met", explains Dr. Peter Baum, who led the team and supervised the experiments. "The duration of each electron pulse, and the time it takes to pass through the region of interest, must both be less than a single oscillation period of the light field." The electron pulses used in the experiment propagate at speeds approximately equal to half the speed of light.
With their novel extension of the principle of the electron microscope, the Munich physicists have shown that it should be feasible to precisely detect and measure even the tiniest and most rapidly oscillating electromagnetic fields. This will allow researchers to obtain a detailed understanding of how transistors or optoelectronic switches operate at the microscopic level.
The new technology is also of interest for the development and analysis of so-called metamaterials. Metamaterials are synthetic, patterned nanostructures, whose permeability and permittivity for electrical and magnetic fields, respectively, deviate fundamentally from those of materials found in nature. This in turn gives rise to novel optical phenomena which cannot be realized in conventional materials. Metamaterials therefore open up entirely new perspectives in optics and optoelectronics, and could provide the basic building blocks for the fabrication of components for light-driven circuits and computers. The new approach to the characterization of electromagnetic waveforms based on the use of attosecond physics brings us a step closer to the electronics of the future.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Luise Dirscherl
49-892-180-3423
Copyright © Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München (LMU)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Physics
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Imaging
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Chip Technology
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Tools
![]() Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
![]() The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








