Home > Press > New tool allows scientists to visualize 'nanoscale' processes
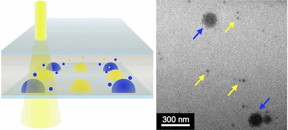 |
| By mixing combinations of gold nanoparticles (yellow arrows) with other nanoscale crystals (blue arrows) in the LCTEM (at left), the chemists showed their technique works. Images by Lucas Parent, UC San Diego |
Abstract:
E-MAIL
Chemists at UC San Diego have developed a new tool that allows scientists for the first time to see, at the scale of five billionths of a meter, "nanoscale" mixing processes occurring in liquids.
New tool allows scientists to visualize 'nanoscale' processes
San Diego, CA | Posted on May 4th, 2016"Being able to look at nanoscale chemical gradients and reactions as they take place is just such a fundamental tool in biology, chemistry and all of material science," said Nathan Gianneschi, a professor of chemistry and biochemistry who headed the team that detailed the development in a paper in this week's issue of the journal Microscopy and Microanalysis. "With this new tool, we'll be able to look at the kinetics and dynamics of chemical interactions that we've never been able to see before."
Scientists have long relied on Transmission Electron Microscopy, or TEM, to see structures at the nanoscale. But that technique can take only static images and the subjects must be dried, or frozen and mounted within a vacuum chamber in order to be seen. As a result, researchers have been unable to view living processes or chemical reactions at the nanoscale, such as the growth and contraction within living cells of tiny fibers or nanoscale protrusions, essential in cell movement and division, or the changes caused by a chemical reaction in a liquid.
"As chemists, we could only really analyze the end products or bulk solution changes, or image at low resolution because we could never see events directly occur at the nanoscale," said Gianneschi.
Recent developments in Liquid Cell TEM, or LCTEM, have allowed scientists to finally take videos of nanoscale objects in liquids. But that technique has been limited by the inability to control the mixing of solutions, a requirement when trying to view and analyze the impact of a drug on a living cell or the reaction of two chemicals.
Joseph Patterson, a postdoctoral researcher in Gianneschi laboratory, working with researchers at SCIENION AG in Germany and Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, has taken a big step to resolving that problem by developing a technique as well as a tool that allows scientists to deposit tiny amounts of liquid -- about 50 trillionths of a liter -- within the viewing area of the LCTEM microscope.
"With this technique, we can view multiple components mixed together at the nanoscale within liquids, so, for example, one could look at biological materials and perhaps see how they respond to a drug," said Gianneschi. "That was never possible before."
"The benefits to basic research are huge," he added. "We will now be able to directly see the growth at the nanoscale of all kinds of things, like natural fibers or microtubules. There's a lot of interest on the part of researchers in understanding how the surfaces of nanoparticles affect chemical reactions or how nanoscale defects on the surfaces of materials develop. We can finally look at the interfaces on nanostructures so that we can optimize the development of new kinds of catalysts, paints and suspensions."
While the scientists have not yet used their tool to view chemical reactions in solution, they have demonstrated that the technique works to provide mixing using combinations of gold nanoparticles and other nanoscale crystals suspended in a liquid.
"What we've demonstrated is the proof of concept," said Gianneschi. "But that's what we'll be doing next."
Although this new tool won't allow scientists to actually view molecules in solution, Gianneschi said they should be able to see the impact of chemical reactions that are occurring on materials that are bigger than five nanometers, or five billionths of a meter.
"We won't be observing molecules colliding, but we will be able to observe single particles and collections of them, on the nanometer length scale," he added. "Observing these kinds of processes has been one of the key challenges in the field of nanoscience."
###
UC San Diego has applied for a patent jointly with SCIENION AG to license the new technique and tool. In addition to Patterson and Gianneschi, other co-authors on the paper are Lucas Parent of UC San Diego, Joshua Cantlon, Holger Eickhoff and Guido Bared of SCIENION AG in Berlin, and James Evans of Pacific Northwest National Laboratory. The study was supported by grants from the U.S. Air Force Office of Scientific Research and the U.S. Army Research Office.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Kim McDonald
858-534-7572
Copyright © University of California, San Diego
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Chemistry
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Imaging
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Tools
![]() Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
![]() The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
Patents/IP/Tech Transfer/Licensing
![]() Getting drugs across the blood-brain barrier using nanoparticles March 3rd, 2023
Getting drugs across the blood-brain barrier using nanoparticles March 3rd, 2023
![]() Metasurfaces control polarized light at will: New research unlocks the hidden potential of metasurfaces August 13th, 2021
Metasurfaces control polarized light at will: New research unlocks the hidden potential of metasurfaces August 13th, 2021
![]() Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals Announces Closing of Agreement with Takeda November 27th, 2020
Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals Announces Closing of Agreement with Takeda November 27th, 2020
Military
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








