Home > Press > University of Illinois researchers create 1-step graphene patterning method
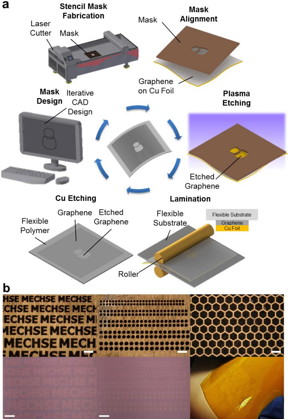 |
| a) This is a schematic illustration of the one-step polymer-free approach to fabricate patterned graphene on a flexible substrate. A stencil mask is designed by computer-aided design software and fabricated by a laser cutter. The fabricated mask is aligned on the as-grown CVD graphene on a Cu foil, and the exposed graphene region is removed by oxygen plasma. The patterned graphene is laminated onto a flexible substrate, followed by etching of the copper foil. b) Optical microscope images and photographs of various stencil masks with sophisticated micro-scale features (top row) and corresponding graphene array patterns transferred onto SiO2 substrate and flexible Kapton film (bottom row). All scale bars: 300 μm. CREDIT: University of Illinois |
Abstract:
Researchers from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have developed a one-step, facile method to pattern graphene by using stencil mask and oxygen plasma reactive-ion etching, and subsequent polymer-free direct transfer to flexible substrates.
University of Illinois researchers create 1-step graphene patterning method
Urbana, IL | Posted on April 27th, 2016Graphene, a two-dimensional carbon allotrope, has received immense scientific and technological interest. Combining exceptional mechanical properties, superior carrier mobility, high thermal conductivity, hydrophobicity, and potentially low manufacturing cost, graphene provides a superior base material for next generation bioelectrical, electromechanical, optoelectronic, and thermal management applications.
"Significant progress has been made in the direct synthesis of large-area, uniform, high quality graphene films using chemical vapor deposition (CVD) with various precursors and catalyst substrates," explained SungWoo Nam, an assistant professor of mechanical science and engineering at Illinois. "However, to date, the infrastructure requirements on post-synthesis processing--patterning and transfer--for creating interconnects, transistor channels, or device terminals have slowed the implementation of graphene in a wider range of applications."
"In conjunction with the recent evolution of additive and subtractive manufacturing techniques such as 3D printing and computer numerical control milling, we developed a simple and scalable graphene patterning technique using a stencil mask fabricated via a laser cutter," stated Keong Yong, a graduate student and first author of the paper, "Rapid Stencil Mask Fabrication Enabled One-Step Polymer-Free Graphene Patterning and Direct Transfer for Flexible Graphene Devices appearing in Scientific Reports.
"Our approach to patterning graphene is based on a shadow mask technique that has been employed for contact metal deposition," Yong added. "Not only are these stencil masks easily and rapidly manufactured for iterative rapid prototyping, they are also reusable, enabling cost-effective pattern replication. And since our approach involves neither a polymeric transfer layer nor organic solvents, we are able to obtain contamination-free graphene patterns directly on various flexible substrates."
Nam stated that this approach demonstrates a new possibility to overcome limitations imposed by existing post-synthesis processes to achieve graphene micro-patterning. Yong envisions this facile approach to graphene patterning sets forth transformative changes in "do It yourself" (DIY) graphene-based device development for broad applications including flexible circuits/devices and wearable electronics.
"This method allows rapid design iterations and pattern replications, and the polymer-free patterning technique promotes graphene of cleaner quality than other fabrication techniques," Nam said. "We have shown that graphene can be patterned into varying geometrical shapes and sizes, and we have explored various substrates for the direct transfer of the patterned graphene."
###
In addition to Nam and Yong, study co-authors include Ali Ashraf and Pilgyu Kang from the Department of Mechanical Science and Engineering at Illinois.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
SungWoo Nam
217-300-0267
Copyright © University of Illinois College of Engineering
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Flexible Electronics
![]() Flexible electronics integrated with paper-thin structure for use in space January 17th, 2025
Flexible electronics integrated with paper-thin structure for use in space January 17th, 2025
![]() Beyond wires: Bubble technology powers next-generation electronics:New laser-based bubble printing technique creates ultra-flexible liquid metal circuits November 8th, 2024
Beyond wires: Bubble technology powers next-generation electronics:New laser-based bubble printing technique creates ultra-flexible liquid metal circuits November 8th, 2024
Software
![]() Visualizing nanoscale structures in real time: Open-source software enables researchers to see materials in 3D while they're still on the electron microscope August 19th, 2022
Visualizing nanoscale structures in real time: Open-source software enables researchers to see materials in 3D while they're still on the electron microscope August 19th, 2022
![]() Luisier wins SNSF Advanced Grant to develop simulation tools for nanoscale devices July 8th, 2022
Luisier wins SNSF Advanced Grant to develop simulation tools for nanoscale devices July 8th, 2022
![]() Oxford Instruments’ Atomfab® system is production-qualified at a market-leading GaN power electronics device manufacturer December 17th, 2021
Oxford Instruments’ Atomfab® system is production-qualified at a market-leading GaN power electronics device manufacturer December 17th, 2021
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








