Home > Press > X-rays and electrons join forces to map catalytic reactions in real-time: New technique combines electron microscopy and synchrotron X-rays to track chemical reactions under real operating conditions
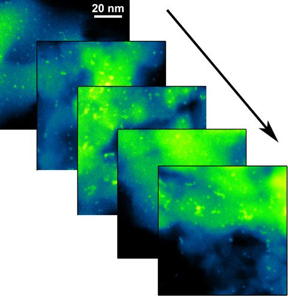 |
| This is a series of scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM) images of platinum nanoparticles, tracking their changes under different atmospheric pressure reaction conditions. CREDIT: Brookhaven National Laboratory |
Abstract:
A new technique pioneered at the U.S. Department of Energy's Brookhaven National Laboratory reveals atomic-scale changes during catalytic reactions in real time and under real operating conditions.
X-rays and electrons join forces to map catalytic reactions in real-time: New technique combines electron microscopy and synchrotron X-rays to track chemical reactions under real operating conditions
Upton, NY | Posted on June 29th, 2015A team of scientists used a newly developed reaction chamber to combine x-ray absorption spectroscopy and electron microscopy for an unprecedented portrait of a common chemical reaction. The results demonstrate a powerful operando technique--from the Latin for "in working condition"--that may revolutionize research on catalysts, batteries, fuel cells, and other major energy technologies.
"We tracked the dynamic transformations of a working catalyst, including single atoms and larger structures, during an active reaction at room temperature," said study coauthor and Brookhaven Lab scientist Eric Stach. "This gives us unparalleled insight into nanoparticle structure and would be impossible to achieve without combining two complementary operando techniques."
The results were published online June 29, 2015, in the journal Nature Communications.
To prove the efficacy of this new mosquito-sized reaction chamber--called a micro-reactor--the scientists tracked the performance of a platinum catalyst during the conversion of ethylene to ethane, a model reaction relevant to many industrial synthesis processes. They conducted x-ray studies at the National Synchrotron Light Source (NSLS) and electron microscopy at the Center for Functional Nanomaterials (CFN), both DOE Office of Science User Facilities.
"The size, shape, and distribution of catalysts affect their efficiency and durability," said study coauthor Ralph Nuzzo of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. "Now that we can track those parameters throughout the reaction sequence, we can better determine the ideal design of future catalysts--especially those that drive energy-efficient reactions without using expensive and rare materials like platinum."
Hidden behind the curtain
In transmission electron microscopy (TEM), a focused electron beam passes through the sample and captures images of the nanoparticles within. This is usually performed in a pristine environment--often an inactive, low-pressure vacuum--but the micro-reactor allowed the TEM to operate in the presence of an atmosphere of reactive gases.
"With TEM, we take high-resolution pictures of the particles to directly see their size and distribution," said Stach, who leads CFN's Electron Microscopy Group. "But with the micro-reactor, some signals were too small to detect. Particles smaller than a single nanometer were hidden behind what we call the resolution curtain of the technique."
Another technique was needed to peer behind the curtain and reveal the full reaction story: x-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS).
In XAS, a beam of x-rays bombards the catalyst sample and deposits energy as it passes through the micro-reactor. The sample then emits secondary x-rays, which are measured to identify its chemical composition--in this instance, the distribution of platinum particles.
"The XAS and TEM data, analyzed together, let us calculate the numbers and average sizes of not one, but several different types of catalysts," said coauthor and Yeshiva University scientist Anatoly Frenkel, who led the x-ray experiments. "Running the tests in an operando condition lets us track broad changes over time, and only the combination of techniques could reveal all catalytic particles."
Versatile micro-reactor
The new micro-reactor was specifically designed and built to work seamlessly with both synchrotron x-rays and electron microscopes.
"Everything was exquisitely controlled at both NSLS and CFN, including precise measurements of the progress of the catalytic reaction," Frenkel said. "For the first time, the operando approach was used to correlate data obtained by different techniques at the same stages of the reaction."
A relatively straightforward mathematical approach allowed them to deduce the total number of ultra-small particles missing in the TEM data.
"We took the full XAS data, which incorporates particles of all sizes, and removed the TEM results covering particles larger than one nanometer--the remainder fills in that crucial sub-nanometer gap in our knowledge of catalyst size and distribution during each step of the reaction," Frenkel said.
Added Stach, "In the past, scientists would look at data before and after the reaction under model conditions, especially with TEM, and make educated guesses. Now we can make definitive statements."
Brighter, faster experiments
The collaboration has already extended this operando micro-reactor approach to incorporate two additional techniques--infrared and Raman spectroscopy--and plans to introduce other complex and complementary x-ray and electron probe techniques over time.
NSLS ended its 32-year experimental run in the fall of 2014, but its successor--the just-opened National Synchrotron Light Source II (NSLS-II)--is 10,000 times brighter and promises to rapidly advance operando science.
"Each round of data collection took six hours at NSLS, but will take just minutes at NSLS-II," Stach said. "Through Laboratory Directed Research and Development funding, we will be part of the initial experiments at the Submicron Resolution X-ray (SRX) Spectroscopy beamline this summer, dramatically increasing the time resolution of the experiments and letting us track changes in a more dynamic fashion. And that's just one of the NSLS-II beamlines where we plan to deploy this technique."
The ethylene to ethane reaction happens at room temperature, but other new micro-reactors can operate at up to 800 degrees Celsius--more than hot enough for most catalytic reactions-- and will increase the versatility and applicability of the approach.
In the near future, this same micro-reactor approach will be used to explore other crucial energy frontiers, including batteries and fuel cells.
"We are seeing the emergence of a very powerful and versatile technique that leverages both NSLS-II and the CFN," said Stach, who was recently named Special Assistant for Operando Experimentation for Brookhaven's Energy Sciences Directorate. "This approach complements the many facilities being developed at Brookhaven Lab for operando energy research. Our goal is to be world leaders in operando science."
####
About Brookhaven National Laboratory
Brookhaven National Laboratory is supported by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov.
One of ten national laboratories overseen and primarily funded by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), Brookhaven National Laboratory conducts research in the physical, biomedical, and environmental sciences, as well as in energy technologies and national security. Brookhaven Lab also builds and operates major scientific facilities available to university, industry and government researchers. Brookhaven is operated and managed for DOE's Office of Science by Brookhaven Science Associates, a limited-liability company founded by the Research Foundation for the State University of New York on behalf of Stony Brook University, the largest academic user of Laboratory facilities, and Battelle, a nonprofit applied science and technology organization.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Justin Eure
631-344-2347
Copyright © Brookhaven National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Chemistry
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Imaging
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Laboratories
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Tools
![]() Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
![]() The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
Energy
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Fuel Cells
![]() Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








