Home > Press > Auto lubricant could rev up speed of medical imaging
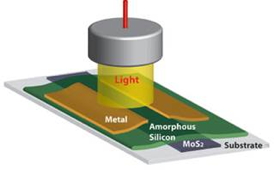 |
| Shown is an experimental photodetector made out of amorphous silicon and molybdenum disulfide (MoS2). The two semiconductors together form a high speed photodetector. Schematic by Mohammad Esmaeili-Rad |
Abstract:
Engineers at the University of California, Berkeley, have built a device that could speed up medical imaging without breaking the bank. The key ingredient? An engine lubricant called molybdenum disulfide, or MoS2, which has been sold in auto parts shops for decades.
Auto lubricant could rev up speed of medical imaging
Berkeley, CA | Posted on August 3rd, 2013Many photodetectors in large-area imaging devices use amorphous silicon because it absorbs light well and is relatively inexpensive to process. But this type of silicon has defects that prevent the fast, ordered movement of electrons, leading to slower operating speeds and more exposure to radiation. Getting better performance requires more expensive, high-temperature processing, adding to the price tag of the imaging device.
Sayeef Salahuddin, UC Berkeley assistant professor of electrical engineering and computer sciences, and postdoctoral scholar Mohammad Esmaeili-Rad solved this problem by pairing a thin film of MoS2 with a sheet of amorphous silicon. Because of the molecular structure of MoS2, the photo-generated electrons it collects are able to move through quickly.
Together, the MoS2 and amorphous silicon formed a diode that resulted in a photoresponse rate that was 10 times faster than conventional amorphous silicon alone.
"Our discovery could bring transformational changes in applications from biomedical imaging to solar cells to energy-efficient transistors," said Salahuddin.
The researchers published their findings today (Friday, Aug. 2) in the open-access journal Scientific Reports.
They point out that because these materials are easy and inexpensive to handle, the cost of speeding up photodetectors would be minimal. Unlike conventional semiconductors like silicon, MoS2 consists of individual nanosheets that can be torn off like pages in a book. These sheets can be used to make thin, novel electronic devices or to improve existing ones.
The National Science Foundation and the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency helped support this work. Esmaeli-Rad's postdoctoral fellowship is supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Sarah Yang
Media Relations
(510) 643-7741
RESEARCHER CONTACT:
Sayeef Salahuddin
(510) 642-4662
Copyright © University of California, Berkeley
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Imaging
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
![]() Observation of left and right at nanoscale with optical force October 6th, 2023
Observation of left and right at nanoscale with optical force October 6th, 2023
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Military
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








