Home > Press > Drawing a line, with carbon nanotubes --New low-cost, durable carbon nanotube sensors can be etched with mechanical pencils
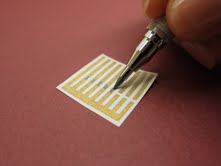 |
| MIT chemists designed a new type of pencil lead consisting of carbon nanotubes, allowing them to draw carbon nanotube sensors onto sheets of paper. Photo: Jan Schnorr |
Abstract:
Carbon nanotubes offer a powerful new way to detect harmful gases in the environment. However, the methods typically used to build carbon nanotube sensors are hazardous and not suited for large-scale production.
Drawing a line, with carbon nanotubes --New low-cost, durable carbon nanotube sensors can be etched with mechanical pencils
Cambridge, MA | Posted on October 9th, 2012A new fabrication method created by MIT chemists — as simple as drawing a line on a sheet of paper — may overcome that obstacle. MIT postdoc Katherine Mirica has designed a new type of pencil lead in which graphite is replaced with a compressed powder of carbon nanotubes. The lead, which can be used with a regular mechanical pencil, can inscribe sensors on any paper surface.
The sensor, described in the journal Angewandte Chemie, detects minute amounts of ammonia gas, an industrial hazard. Timothy Swager, the John D. MacArthur Professor of Chemistry and leader of the research team, says the sensors could be adapted to detect nearly any type of gas.
"The beauty of this is we can start doing all sorts of chemically specific functionalized materials," Swager says. "We think we can make sensors for almost anything that's volatile."
Other authors of the paper are graduate student Jonathan Weis and postdocs Jan Schnorr and Birgit Esser.
Pencil it in
Carbon nanotubes are sheets of carbon atoms rolled into cylinders that allow electrons to flow without hindrance. Such materials have been shown to be effective sensors for many gases, which bind to the nanotubes and impede electron flow. However, creating these sensors requires dissolving nanotubes in a solvent such as dichlorobenzene, using a process that can be hazardous and unreliable.
Swager and Mirica set out to create a solvent-free fabrication method based on paper. Inspired by pencils on her desk, Mirica had the idea to compress carbon nanotubes into a graphite-like material that could substitute for pencil lead.
To create sensors using their pencil, the researchers draw a line of carbon nanotubes on a sheet of paper imprinted with small electrodes made of gold. They then apply an electrical current and measure the current as it flows through the carbon nanotube strip, which acts as a resistor. If the current is altered, it means gas has bound to the carbon nanotubes.
The researchers tested their device on several different types of paper, and found that the best response came with sensors drawn on smoother papers. They also found that the sensors give consistent results even when the marks aren't uniform.
Two major advantages of the technique are that it is inexpensive and the "pencil lead" is extremely stable, Swager says. "You can't imagine a more stable formulation. The molecules are immobilized," he says.
Sensors for any gas
In this study, the researchers focused on pure carbon nanotubes, but they are now working on tailoring the sensors to detect a wide range of gases. Selectivity can be altered by adding metal atoms to the nanotube walls, or by wrapping polymers or other materials around the tubes.
One gas the researchers are particularly interested in is ethylene, which would be useful for monitoring the ripeness of fruit as it is shipped and stored. The team is also pursuing sensors for sulfur compounds, which might prove helpful for detecting natural gas leaks.
The research was funded by the Army Research Office through MIT's Institute for Soldier Nanotechnologies and a National Institutes of Health fellowship to Mirica.
Written by Anne Trafton, MIT News Office
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Caroline McCall
MIT News Office
T: 617-253-1682
Copyright © MIT
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Videos/Movies
![]() New X-ray imaging technique to study the transient phases of quantum materials December 29th, 2022
New X-ray imaging technique to study the transient phases of quantum materials December 29th, 2022
![]() Solvent study solves solar cell durability puzzle: Rice-led project could make perovskite cells ready for prime time September 23rd, 2022
Solvent study solves solar cell durability puzzle: Rice-led project could make perovskite cells ready for prime time September 23rd, 2022
![]() Scientists prepare for the world’s smallest race: Nanocar Race II March 18th, 2022
Scientists prepare for the world’s smallest race: Nanocar Race II March 18th, 2022
![]() Visualizing the invisible: New fluorescent DNA label reveals nanoscopic cancer features March 4th, 2022
Visualizing the invisible: New fluorescent DNA label reveals nanoscopic cancer features March 4th, 2022
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings
![]() Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
![]() Detection of bacteria and viruses with fluorescent nanotubes July 21st, 2023
Detection of bacteria and viruses with fluorescent nanotubes July 21st, 2023
Sensors
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Military
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








