Home > Press > Hot off the Press: Nanoscale Gutenberg-style printing
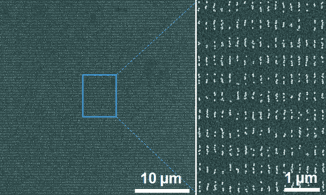 |
| © Wiley-VCH |
Abstract:
When Gutenberg developed the principles of modern book printing, books became available to the masses. Hoping to bring technology capable of mass production to the nanometer scale, Udo Bach and this team of scientists at Monash University (Australia) and the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (USA) have developed a nanoprinting process modeled on Gutenberg's printing method. Their goal is the simple, inexpensive production of nanotechnological components for solar cells, biosensors, and other electronic systems. As the researchers report in the journal Angewandte Chemie, their "ink" consists of gold nanoparticles, and the specific bonding between DNA molecules ensures its transfer to the substrate.
Hot off the Press: Nanoscale Gutenberg-style printing
Australia | Posted on April 15th, 2011Nanopatterns with extremely high resolution are not difficult to produce with today's technology. However, the methods used so far are analogous those used to produce the hand-written books of the era before Gutenberg; they are too slow and work-intensive for commercial fabrication. "New nanoprinting techniques offer an interesting solution," says Bach. Along with co-workers, he has developed a process that works with a reusable "printing plate".
The printing plate is a silicon wafer—like those used for the production of computer chips—that has been coated with a photoresist and covered with a mask. The wafer is then exposed to an electron beam (electron beam lithography). In the areas exposed to the beam, the photoresist is removed, exposing the wafer for etching. The wafer is then coated with gold. When the photoresist layer is removed, the gold only sticks to the etched areas. Polyethylene glycol chains are then bound specifically to the gold through sulfur-hydrogen groups. The chains have positively charged amino groups at their ends. The completed printing plate is then dipped into the "ink", a solution of gold nanoparticles coated with negatively charged DNA molecules. Electrostatic attraction causes the DNA to stick to the amino groups, binding the gold nanoparticles to the gold-patterned areas of the printing plate.
The "paper" is a silicon wafer coated with a whisper-thin gold film and a layer of DNA. These DNA strands are complementary to those on the gold nanoparticles, with which they pair up to form double strands. This type of bond is stronger than the electrostatic attraction between the DNA and the amino groups. When the "paper" is pressed onto the "printing plate" and then removed, the gold nanoparticles from the ink remain stuck to the "paper" in the desired pattern. The "printing plate" can be cleaned and reused multiple times. Says Bach: "Our results demonstrate that it is possible to produce affordable printed elements based on nanoparticles."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Udo Bach
Monash University
Clayton (Australia)
Phone:+61 3 990 56264
Copyright © ohn Wiley & Sons, Inc.
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Sensors
Nanoelectronics
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
![]() Atomic level deposition to extend Moore’s law and beyond July 15th, 2022
Atomic level deposition to extend Moore’s law and beyond July 15th, 2022
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() Charged “molecular beasts” the basis for new compounds: Researchers at Leipzig University use “aggressive” fragments of molecular ions for chemical synthesis November 3rd, 2023
Charged “molecular beasts” the basis for new compounds: Researchers at Leipzig University use “aggressive” fragments of molecular ions for chemical synthesis November 3rd, 2023
Printing/Lithography/Inkjet/Inks/Bio-printing/Dyes
![]() Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
![]() Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
![]() Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








