Home > Press > Scientists Discover Magnetic Superatoms
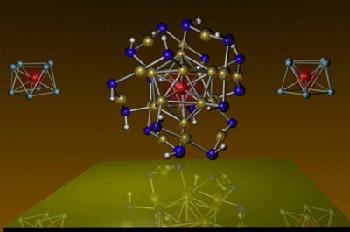 |
| VCs8 and MnAu24(SH)18 magnetic superatoms that mimic a manganese atom. The MnAu24 cluster is surrounded by sulfur and hydrogen atoms to protect it against outside attack, thus making it valuable for use in biomedical applications. Image courtesy of Ulises Reveles, Ph.D, VCU. |
Abstract:
A team of Virginia Commonwealth University scientists has discovered a ‘magnetic superatom' - a stable cluster of atoms that can mimic different elements of the periodic table - that one day may be used to create molecular electronic devices for the next generation of faster computers with larger memory storage.
Scientists Discover Magnetic Superatoms
Richmond, VA | Posted on June 16th, 2009The newly discovered cluster, consisting of one vanadium and eight cesium atoms, acts like a tiny magnet that can mimic a single manganese atom in magnetic strength while preferentially allowing electrons of specific spin orientation to flow through the surrounding shell of cesium atoms. The findings appear online in the journal Nature Chemistry.
Through an elaborate series of theoretical studies, Shiv N. Khanna, Ph.D., professor in the VCU Department of Physics, together with VCU postdoctoral associates J. Ulises Reveles, A.C. Reber, and graduate student P. Clayborne, and collaborators at the Naval Research Laboratory in D.C., and the Harish-Chandra Research Institute in Allahabad, India, examined the electronic and magnetic properties of clusters having one vanadium atom surrounded by multiple cesium atoms.
They found that when the cluster had eight cesium atoms it acquired extra stability due to a filled electronic state. An atom is in a stable configuration when its outermost shell is full. Consequently, when an atom combines with other atoms, it tends to lose or gain valence electrons to acquire a stable configuration.
According to Khanna, the new cluster had a magnetic moment of five Bohr magnetons, which is more than twice the value for an iron atom in a solid iron magnet. A magnetic moment is a measure of the internal magnetism of the cluster. A manganese atom also has a similar magnetic moment and a closed electronic shell of more tightly bound electrons, and Khanna said that the new cluster could be regarded as a mimic of a manganese atom.
"An important objective of the discovery was to find what combination of atoms will lead to a species that is stable as we put multiple units together. The combination of magnetic and conducting attributes was also desirable. Cesium is a good conductor of electricity and hence the superatom combines the benefit of magnetic character along with ease of conduction through its outer skin," Khanna said.
"A combination such as the one we have created here can lead to significant developments in the area of "molecular electronics," a field where researchers study electric currents through small molecules. These molecular devices are expected to help make non-volatile data storage, denser integrated devices, higher data processing and other benefits," he said.
Khanna and his team are conducting preliminary studies on molecules composed of two such superatoms and have made some promising observations that may have applications in spintronics. Spintronics is a process using electron spin to synthesize new devices for memory and data processing.
The researchers have also proposed that by combining gold and manganese, one can make other superatoms that have magnetic moment, but will not conduct electricity. These superatoms may have potential biomedical applications such as sensing, imaging and drug delivery.
This research was supported by the U.S. Department of the Army.
EDITOR'S NOTE: A copy of the study is available for reporters in PDF format by email request from the Nature Publishing Group press office by contacting
####
About Virginia Commonwealth University
Virginia Commonwealth University is the largest university in Virginia with national and international rankings in sponsored research. Located on two downtown campuses in Richmond, VCU enrolls 32,000 students in 205 certificate and degree programs in the arts, sciences and humanities. Sixty-five of the programs are unique in Virginia, many of them crossing the disciplines of VCU’s 15 schools and one college. MCV Hospitals and the health sciences schools of Virginia Commonwealth University compose the VCU Medical Center, one of the nation’s leading academic medical centers.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Sathya Achia Abraham
VCU Communications and Public Relations
(804) 827-0890
Copyright © Virginia Commonwealth University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
![]() Linearly assembled Ag-Cu nanoclusters: Spin transfer and distance-dependent spin coupling November 4th, 2022
Linearly assembled Ag-Cu nanoclusters: Spin transfer and distance-dependent spin coupling November 4th, 2022
Memory Technology
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Researchers discover materials exhibiting huge magnetoresistance June 9th, 2023
Researchers discover materials exhibiting huge magnetoresistance June 9th, 2023
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Sensors
Nanoelectronics
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
![]() Atomic level deposition to extend Moore’s law and beyond July 15th, 2022
Atomic level deposition to extend Moore’s law and beyond July 15th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








