Home > Press > Stability of perovskite solar cells reaches next milestone
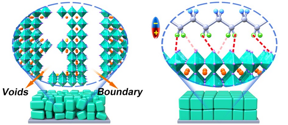 |
| In the control perovskite layer (left), the microcrystals are not perfectly ordered and voids can form. In the new variant (right), the dipolar polymer cushions the tiny crystals and thus reduces the thermomechanical stress. CREDIT G. Li/HZB |
Abstract:
The material class of halide perovskites is seen as a great hope for even more solar power at even lower costs. The materials are very cheap, can be processed into thin films with minimal energy input and achieve already efficiencies that are significantly higher than those of conventional silicon solar cells.
Stability of perovskite solar cells reaches next milestone
Berlin, Germany | Posted on January 27th, 2023The Goal: 20 Years Outdoor Stability
However, solar modules are expected to provide stable output for at least 20 years in outdoor conditions while exposed to large temperature fluctuations. Silicon PV manages this easily, whereas the semi-organic perovskites lose performance rather fast. "Sunlight can heat up the inside of a PV cell to 80 Celsius; in the dark, the cell then cools down immediately to the outside temperature. This triggers large mechanical stresses in the thin layer of perovskite microcrystals, creating defects and even local phase transitions, so that the thin film loses its quality," explains Prof. Antonio Abate, who heads a large group at HZB.
Chemical Variations examined
Together with his team and a number of international partners, he has investigated a chemical variation that significantly improves the stability of the perovskite thin film in different solar cell architectures, among them the p-i-n architecture, which normally is a little less efficient than the more often used n-i-p architecture.
A "Soft Shell" against Stress
"We optimized the device structure and process parameters, building upon previous results, and finally could achieve a decisive improvement with b-poly(1,1-difluoroethylene) or b-pV2F for short," says Guixiang Li, who is doing his PhD supervised by Prof. Abate. b-pV2F molecules resemble a zigzag chain occupied by alternating dipoles. "This polymer seems to wrap around the individual perovskite microcrystals in the thin film like a soft shell, creating a kind of cushion against thermomechanical stress," Abate explains.
Record Efficiency for p-i-n Architecture 24,6%
In fact, scanning electron microscope images show that in the cells with b-pV2F, the tiny granules nestle a little closer. "In addition, the dipole chain of b-pV2F improves the transport of charge carriers and thus increases the efficiency of the cell," says Abate. Indeed they produced cells on a laboratory scale with efficiencies of up to 24.6%, which is a record for the p-i-n architecture.
One Year Outdoor Use
The newly produced solar cells were subjected over a hundred cycles between +80 Celsius and -60 Celsius and 1000 hours of continuous 1-sun equivalent illumination. That corresponds to about one year of outdoor use. "Even under these extreme stresses, they still achieved 96 % efficiency in the end," Abate emphasises. That is already in the right order of magnitude. If it is now feasible to reduce the losses a little further, perovskite solar modules could still produce most of their original output after 20 years - this goal is now coming within reach.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Antonia Roetger
Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin für Materialien und Energie
Office: 0049-308-062-43733
Copyright © Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin für Materialien und Energie
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Perovskites
![]() Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
News and information
![]() New organic molecule shatters phosphorescence efficiency records and paves way for rare metal-free applications July 5th, 2024
New organic molecule shatters phosphorescence efficiency records and paves way for rare metal-free applications July 5th, 2024
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() New method cracked for high-capacity, secure quantum communication July 5th, 2024
New method cracked for high-capacity, secure quantum communication July 5th, 2024
![]() Searching for dark matter with the coldest quantum detectors in the world July 5th, 2024
Searching for dark matter with the coldest quantum detectors in the world July 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() New method cracked for high-capacity, secure quantum communication July 5th, 2024
New method cracked for high-capacity, secure quantum communication July 5th, 2024
![]() Searching for dark matter with the coldest quantum detectors in the world July 5th, 2024
Searching for dark matter with the coldest quantum detectors in the world July 5th, 2024
![]() Atomic force microscopy in 3D July 5th, 2024
Atomic force microscopy in 3D July 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
![]() A New Blue: Mysterious origin of the ribbontail ray’s electric blue spots revealed July 5th, 2024
A New Blue: Mysterious origin of the ribbontail ray’s electric blue spots revealed July 5th, 2024
![]() New organic molecule shatters phosphorescence efficiency records and paves way for rare metal-free applications July 5th, 2024
New organic molecule shatters phosphorescence efficiency records and paves way for rare metal-free applications July 5th, 2024
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() New organic molecule shatters phosphorescence efficiency records and paves way for rare metal-free applications July 5th, 2024
New organic molecule shatters phosphorescence efficiency records and paves way for rare metal-free applications July 5th, 2024
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() New method cracked for high-capacity, secure quantum communication July 5th, 2024
New method cracked for high-capacity, secure quantum communication July 5th, 2024
![]() Searching for dark matter with the coldest quantum detectors in the world July 5th, 2024
Searching for dark matter with the coldest quantum detectors in the world July 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() New method cracked for high-capacity, secure quantum communication July 5th, 2024
New method cracked for high-capacity, secure quantum communication July 5th, 2024
![]() Searching for dark matter with the coldest quantum detectors in the world July 5th, 2024
Searching for dark matter with the coldest quantum detectors in the world July 5th, 2024
![]() Atomic force microscopy in 3D July 5th, 2024
Atomic force microscopy in 3D July 5th, 2024
Energy
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() Charged “molecular beasts” the basis for new compounds: Researchers at Leipzig University use “aggressive” fragments of molecular ions for chemical synthesis November 3rd, 2023
Charged “molecular beasts” the basis for new compounds: Researchers at Leipzig University use “aggressive” fragments of molecular ions for chemical synthesis November 3rd, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








