Home > Press > An alternative to MINFLUX that enables nanometre resolution in a confocal microscope
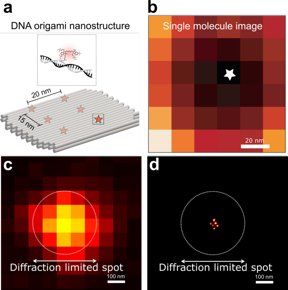 |
| a. Schematic of the DNA origami used to place six fluorophores in a rectangular arrangement. b. Image of a single molecule obtained with RASTMIN. c. Diffraction limited image of the DNA origami. d. Super resolved image of the DNA origami using RASTMIN. CREDIT by Luciano A. Masullo, Alan M. Szalai, Lucía F. Lopez, Mauricio Pilo-Pais, Guillermo P. Acuna, and Fernando D. Stefani |
Abstract:
Fluorescence microscopy is a major workhorse in life sciences, biophysics, and physical chemistry, as it allows visualization with great specificity and sensitivity. In particular, the detection of single fluorescent molecules has been used to provide information beyond ensemble averages with applications in different fields of research. For example, super-resolution methods based on the localization of single emitters have been used in the last 15 years to study biological systems with unprecedented spatial resolution in the 10-50 nm range, and even enabling the discovery of supramolecular cellular structures. On the other hand, single-molecule tracking has enabled to study individual trajectories of relevant targets that would be otherwise hidden in the average behaviour of an ensemble of unsynchronized molecules.
An alternative to MINFLUX that enables nanometre resolution in a confocal microscope
Changchun, China | Posted on August 26th, 2022Most commonly, the position of a single fluorescent molecule is obtained from a fit to its image recorded in a scientific camera. However, this kind of approaches can barely surpass the 10-nm resolution barrier because of the photostability of the fluorescent dyes. In this way, the closest environment around a target (with typical size of 1-5 nm) cannot be interrogated. Alternatively, other approaches infer the molecular position from the signal registered upon excitation with a sequence of spatially shifted patterns of light. These methods, particularly when using a minimum of light intensity, have been demonstrated to be more efficient to obtain the molecular coordinates. In particular, the so-called MINFLUX technique has been proved to achieve 1-2 nm localization precision with moderate number of photons. However, the high technical complexity of MINFLUX and other related techniques has hampered its widespread application.
In a new paper published in Light: Science & Applications, a team of scientists, led by Professor Fernando Stefani from Centro de Investigaciones en Bionanociencias (CIBION), Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET, Argentina), in cooperation with the group of Prof. Guillermo Acuna at the University of Fribourg (Switzerland), have developed RASTMIN, a method that delivers equivalent resolution to MINFLUX, but can be implemented in standard confocal microscopes. In RASTMIN, only two main modifications to a confocal microscope need to be implemented. On the one hand, a doughnut-shaped focus has to be generated. On the other hand, the sample needs to be actively stabilized relative to the optical system. Apart from these two conditions, that are also needed in MINFLUX, no further modifications are required. For example, RASTMIN uses scanning and data acquisition routines available in any standard confocal microscope, and hence the control software already installed in any confocal setup can still be used to perform RASTMIN.
In the paper, the authors demonstrate the performance of RASTMIN by obtaining super-resolved images of fluorophores in a tailored DNA nanostructures (a DNA origami) achieving a localization precision of 1-2 nm. They also combine RASTMIN with fluorescence lifetime imaging.
The authors anticipate that RASTMIN will pave the route to new discoveries in life sciences:
“The structure and function of biological matter is shaped through the assembly and interaction of biomolecules at the nanoscale. In some cases, changing the spatial arrangement of certain proteins in the nanometer scale, or even changing the conformational state of a single protein can lead to a biological response of an entire cell. So far, fluorescence imaging with nanometer-scale resolution has been limited to a reduced number of expert groups. With RASTMIN, because it can be easily implemented in existing laser-scanning microscopes, we foresee that many more groups will now access to this new regime of spatial resolution, increasing the number of biological questions addressed and discoveries.” said Professor Stefani.
“Of course, fully exploiting the resolution power of RASTMIN will raise new challenges. For example, it will require the implementation of labeling strategies that do not artificially increase the size of the target molecules. This is a general issue for molecular-scale resolution techniques, and many labs around the world are currently devoting efforts to develop labeling strategies that minimize this problem. We expect that the introduction of RASTMIN will represent a breakthrough since it will make nm-scale nanoscopy accessible to a significantly broader community, encouraging scientists from different fields to develop tools to keep improving and easing this type of techniques.”
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Yaobiao Li
Light Publishing Center, Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics And Physics, CAS
Office: 86-431-861-76851
Expert Contact
Fernando D. Stefani
Universidad de Buenos Aires, Argentina
Copyright © Light Publishing Center, Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics And Physics, CAS
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Tools
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
![]() Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








