Home > Press > Viral RNA sensing: Optical detection of picomolar concentrations of RNA using switches in plasmonic chirality
 |
Abstract:
Even tiny amounts of viruses can have disastrous consequences. RNA identification can reveal the type of virus present. A fast and sensitive technique based on optical detection has now been outlined in the journal Angewandte Chemie. Scientists from Germany and Finland have demonstrated the binding of an RNA target to a probe made of gold nanorods and a DNA origami structure. Chirality switches triggered by binding can be measured by circular dichroism spectroscopy.
Viral RNA sensing: Optical detection of picomolar concentrations of RNA using switches in plasmonic chirality
MALDEN, MA | Posted on September 21st, 2018Identifying the pathogen--often a virus--that is troubling a patient is among the biggest challenges in healthcare. Viruses responsible for Zika fever, AIDS, and hepatitis C contain mutating RNA sequences. Physicians need to know quickly which type of virus their patients have acquired, but current techniques based on multiplying RNA are costly and time-consuming. Now, Tim Liedl from Ludwigs-Maximilians-Universität in Munich, Germany, and his colleagues, have developed a fast detection strategy based on nanoplasmonics, DNA origami, and an optical readout.
Light can induce plasmonic waves in nanosized metal structures smaller than the wavelength of the incident light. This resonance may lead to strongly enhanced light emission even from nanoscopic structures--a feature that is highly interesting for biosensing applications. Liedl and colleagues have created a nanosized sensing probe for RNA molecules.
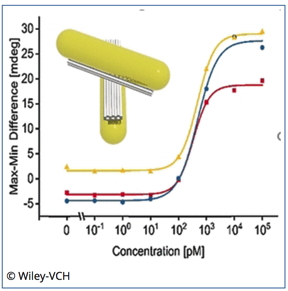
The probe, a nanosized apparatus made of DNA and gold nanorods, was assembled by the so-called DNA origami technique, which exploits the specific interactions of the DNA bases to fold and glue together single strands in any desired form. The authors constructed two bars of parallel DNA helices loosely connected through a hinge in the middle of the bars. Gold nanorods were placed on top of each of the crossed bars. Both crossing arms were supplied with functionality at their ends: the scientists attached one single DNA sequence complemented with a blocking strand to one arm, and the complementing DNA sequence to the other. In the presence of target RNA, which could be a typical viral RNA sequence, the blocking strand would leave its DNA in favor of RNA hybridization, and both single DNA sequences would complementarily form a double strand whereby the two arms of the cross are pulled together. This structural change introduces chirality to the probe.
Chirality can be detected with circular dichroism. And indeed, the structural changes triggered by the RNA binding induced a circular dichroism signal detectable with a CD spectrometer. Concentrations as low as 100 picomolar of the target RNA were recognized, according to the authors. The scientists hope to establish this technique in lab-on-a-chip systems where few steps are required for sample preparation and low-cost miniature devices lead to sensitive results. Preliminary results on serum from blood with added viral RNA were promising.
The authors admit that the detection limits are still not low enough to be clinically relevant. However, they believe improvements should be possible; including, better protection of the nanosensors from serum proteins, a change to better resonating plasmonic metals, and expansion of RNA recognition sites. This could make the technique a promising diagnostic tool that is not necessarily limited to viral RNA.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Mario Mueller
Copyright © Wiley
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








