Home > Press > Nanostructures taste the rainbow: Combining nanophotonics and thermoelectrics, engineers at Caltech generate materials capable of distinguishing between tiny differences in wavelengths of light
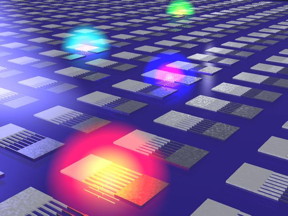 |
| This is an artist's representation of a conceptual design for the color detector, which uses thermoelectric structures with arrays of nanoscale wires that absorb different wavelengths of light based on their width. CREDIT Harry Atwater and Kelly Mauser/Caltech |
Abstract:
Engineers at Caltech have for the first time developed a light detector that combines two disparate technologies -- nanophotonics, which manipulates light at the nanoscale, and thermoelectrics, which translates temperature differences directly into electron voltage -- to distinguish different wavelengths (colors) of light, including both visible and infrared wavelengths, at high resolution.
Nanostructures taste the rainbow: Combining nanophotonics and thermoelectrics, engineers at Caltech generate materials capable of distinguishing between tiny differences in wavelengths of light
Pasadena. CA | Posted on June 30th, 2017Light detectors that distinguish between different colors of light or heat are used in a variety of applications, including satellites that study changing vegetation and landscape on the earth and medical imagers that distinguish between healthy and cancerous cells based on their color variations.
The new detector, described in a paper in Nature Nanotechnology on May 22, operates about 10 to 100 times faster than current comparable thermoelectric devices and is capable of detecting light across a wider range of the electromagnetic spectrum than traditional light detectors. In traditional light detectors, incoming photons of light are absorbed in a semiconductor and excite electrons that are captured by the detector. The movement of these light-excited electrons produces an electric current -- a signal -- that can be measured and quantified. While effective, this type of system makes it difficult to "see" infrared light, which is made up of lower-energy photons than those in visible light.
Because the new detectors are potentially capable of capturing infrared wavelengths of sunlight and heat that cannot be collected efficiently by conventional solar materials, the technology could lead to better solar cells and imaging devices.
"In nanophotonics, we study the way light interacts with structures that are much smaller than the optical wavelength itself, which results in extreme confinement of light. In this work, we have combined this attribute with the power conversion characteristics of thermoelectrics to enable a new type of optoelectronic device," says Harry Atwater, corresponding author of the study. Atwater is the Howard Hughes Professor of Applied Physics and Materials Science in the Division of Engineering and Applied Science at Caltech, and director of the Joint Center for Artificial Photosynthesis (JCAP). JCAP is a Department of Energy (DOE) Energy Innovation Hub focused on developing a cost-effective method of turning sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into fuel. It is led by Caltech with Berkeley Lab as a major partner.
Atwater's team built materials with nanostructures that are hundreds of nanometers wide -- smaller even than the wavelengths of light that represent the visible spectrum, which ranges from about 400 to 700 nanometers.
The researchers created nanostructures with a variety of widths, that absorb different wavelengths -- colors -- of light. When these nanostructures absorb light, they generate an electric current with a strength that corresponds to the light wavelength that is absorbed.
The detectors were fabricated in the Kavli Nanoscience Institute cleanroom at Caltech, where the team created subwavelength structures using a combination of vapor deposition (which condenses atom-thin layers of material on a surface from an element-rich mist) and electron beam lithography (which then cuts nanoscale patterns in that material using a focused beam of electrons). The structures, which resonate and generate a signal when they absorb photons with specific wavelengths, were created from alloys with well-known thermoelectric properties, but the research is applicable to a wide range of materials, the authors say.
"This research is a bridge between two research fields, nanophotonics and thermoelectrics, that don't often interact, and creates an avenue for collaboration," says graduate student Kelly Mauser (MS '16), lead author of the Nature Nanotechnology study. "There is a plethora of unexplored and exciting application and research opportunities at the junction of these two fields."
###
The study is titled "Resonant thermoelectric nanophotonics." Coauthors from Caltech include Keith Schwab, professor of applied physics; Ragip Pala, senior research scientist; graduate student Dagny Fleischman; and postdoctoral researchers Seyoon Kim and Slobodan Mitrovic. This research was funded by DOE Office of Science grant DE-FG02-07ER46405.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Robert
626-395-1862
Copyright © California Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Environment
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Aerospace/Space
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








