Home > Press > Block copolymer micellization as a protection strategy for DNA origami
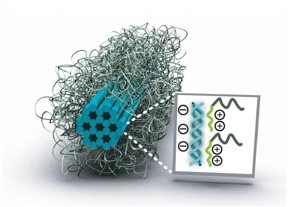 |
| DNA origami. CREDIT cfaed |
Abstract:
The precise positioning of individual molecules with respect to one another is fundamentally challenging. DNA Nanotechnology enables the synthesis of nanometer-sized objects with programmable shapes out of many chemically produced DNA fragments. One of the most widely used methods in this field is called "DNA origami" which allows to fabricate nanoparticles with almost arbitrary shapes, which are around a thousand-fold smaller than the diameter of a human hair. They can be site-specifically functionalized with a large variety of materials such as individual protein molecules, antibodies, drugs molecules or inorganic nanoparticles. This allows to place them in defined geometries or distances with nanometer precision.
Block copolymer micellization as a protection strategy for DNA origami
Dresden, Germany | Posted on March 17th, 2017Due to this unique control over matter on the nanometer-scale, DNA nanostructures have also been considered for applications in molecular biology and nanomedicine. For example, they can be used as programmable drug carriers, diagnostic devices or to study the response of cells to precisely arranged molecules. However, many of these artificial DNA nanostructures need a much higher salt concentration than that in bodily fluids or cell culture buffers to maintain their structure and thus their functionality. Moreover, they can be degraded quickly by special enzymes (nucleases) that are present in bodily fluids such as saliva or blood that digest foreign DNA. This instability limits any biological or medical applications.
To overcome this deficiency, a team led by cfaed Research Group Leader Dr. Thorsten L. Schmidt (Technische Universität Dresden / Germany) coated several different DNA origami structures with a synthetic polymer. This polymer consists of two segments, a short positively charged segment which electrostatically "glues" the polymer to the negatively charged DNA nanostructure and a long uncharged polymer chain that covers the entire nanostructure resembling a fur. In their study "Block Copolymer Micellization as a Protection Strategy for DNA Origami" published in Angewandte Chemie [DOI: 10.1002/anie.201608873] they showed that such DNA nanostructures covered with the polymers were protected against nuclease digestion and low salt conditions. Furthermore they showed that structures functionalized with nanoparticles can be protected by the same mechanism.
This straightforward, cost-effective and robust route to protect DNA-based structures could therefore enable applications in biology and nanomedicine, where un-protected DNA origami would be degraded.
About cfaed
cfaed is a microelectronics research cluster funded by the German Excellence Initiative. It comprises 11 cooperating institutes in Saxony. About 300 scientists from more than 20 countries investigate new technologies for electronic information processing. These technologies are inspired by innovative materials such as silicon nanowires, carbon nanotubes or polymers or based on completely new concepts such as the chemical chip or circuit fabrication methods by self-assembling structures such as DNA-Origami. The orchestration of these new devices into heterogeneous information processing systems with focus on their resilience and energy-efficiency is also part of cfaed's research program which comprises nine different research paths. http://www.cfaed.tu-dresden.de
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Matthias Hahndorf
49-035-146-342-847
Thorsten-Lars Schmidt, PhD.
Group Leader DNA Chemistry
Copyright © Technische Universität Dresden
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








