Home > Press > Quantum experiments designed by machines: Algorithm does not work intuitive -- just as quantum physics
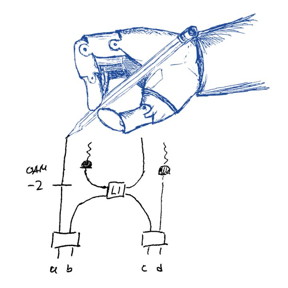 |
| The algorithm Melvin found out that the most simple realization can be asymmetric and therefore counterintuitive.
Copyright: Robert Fickler, Universität Wien |
Abstract:
Quantum physicist Mario Krenn and his colleagues in the group of Anton Zeilinger from the Faculty of Physics at the University of Vienna and the Austrian Academy of Sciences have developed an algorithm which designs new useful quantum experiments. As the computer does not rely on human intuition, it finds novel unfamiliar solutions. The research has just been published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
Quantum experiments designed by machines: Algorithm does not work intuitive -- just as quantum physics
Vienna, Austria | Posted on February 23rd, 2016The idea was developed when the physicists wanted to create new quantum states in the laboratory, but were unable to conceive of methods to do so. "After many unsuccessful attempts to come up with an experimental implementation, we came to the conclusion that our intuition about these phenomena seems to be wrong. We realized that in the end we were just trying random arrangements of quantum building blocks. And that is what a computer can do as well - but thousands of times faster", explains Mario Krenn, PhD student in Anton Zeilinger's group and first author research.
After a few hours of calculation, their algorithm - which they call Melvin - found the recipe to the question they were unable to solve, and its structure surprised them. Zeilinger says: "Suppose I want build an experiment realizing a specific quantum state I am interested in. Then humans intuitively consider setups reflecting the symmetries of the state. Yet Melvin found out that the most simple realization can be asymmetric and therefore counterintuitive. A human would probably never come up with that solution."
The physicists applied the idea to several other questions and got dozens of new and surprising answers. "The solutions are difficult to understand, but we were able to extract some new experimental tricks we have not thought of before. Some of these computer-designed experiments are being built at the moment in our laboratories", says Krenn.
Melvin not only tries random arrangements of experimental components, but also learns from previous successful attempts, which significantly speeds up the discovery rate for more complex solutions. In the future, the authors want to apply their algorithm to even more general questions in quantum physics, and hope it helps to investigate new phenomena in laboratories.
###
The research was supported by Austrian Academy of Sciences (ÖAW), the European Research Council (SIQS Grant No. 600645 EUFP7-ICT), the Austrian Science Fund (FWF) with SFB F40 (FOQUS).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Mario Krenn
43-142-772-9568
Copyright © University of Vienna
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Publication in Physical Review Letters
Publication in Physical Review Letters
| Related News Press |
Quantum Physics
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








