Home > Press > Chemists strike nano-gold: 4 new atomic structures for gold nanoparticle clusters: Research builds upon work by Nobel Prize-winning team from Stanford University
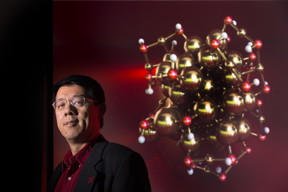 |
| Xiao Cheng Zeng, chemistry professor at the University of Nebraska-Lincoln, is shown with a model of a gold nano-cluster. CREDIT: Craig Chandler/University Communications/University of Nebraska-Lincoln |
Abstract:
Arranging gold, atomic staples and electron volts, chemists have drafted new nanoscale blueprints for low-energy structure capable of housing pharmaceuticals and oxygen atoms.
Chemists strike nano-gold: 4 new atomic structures for gold nanoparticle clusters: Research builds upon work by Nobel Prize-winning team from Stanford University
Lincoln, NE | Posted on April 28th, 2015Led by University of Nebraska-Lincoln chemistry professor Xiao Cheng Zeng, and former UNL visiting professor Yi Gao, new research has revealed four atomic arrangements of a gold nanoparticle cluster. The arrangements exhibit much lower potential energy and greater stability than a standard-setting configuration reported last year by a Nobel Prize-winning team from Stanford University.
The modeling of these arrangements could inform the cluster's use as a transporter of pharmaceutical drugs and as a catalyst for removing pollutants from vehicular emissions or other industrial byproducts, Zeng said.
Zeng and his colleagues unveiled the arrangements for a molecule featuring 68 gold atoms and 32 pairs of bonded sulfur-hydrogen atoms. Sixteen of the gold atoms form the molecule's core; the remainder bond with the sulfur and hydrogen to form a protective coating that stems from the core.
Differences in atomic arrangements can alter molecular energy and stability, with less potential energy making for a more stable molecule. The team calculates that one of the arrangements may represent the most stable possible structure in a molecule with its composition.
"Our group has helped lead the front on nano-gold research over the past 10 years," said Zeng, an Ameritas University Professor of chemistry. "We've now found new coating structures of much lower energy, meaning they are closer to the reality than (previous) analyses. So the deciphering of this coating structure is major progress."
The researchers reported their findings in the April 24 edition of Science Advances, an online journal from the American Association for the Advancement of Science.
The structure of the molecule's gold core was previously detailed by the Stanford team. Building on this, Zeng and his colleagues used a computational framework dubbed "divide-and-protect" to configure potential arrangements of the remaining gold atoms and sulfur-hydrogen pairs surrounding the core.
The researchers already knew that the atomic coating features staple-shaped linkages of various lengths. They also knew the potential atomic composition of each short, medium and long staple -- such as the fact that a short staple consists of two sulfur atoms bonded with one gold.
By combining this information with their knowledge of how many atoms reside outside the core, the team reduced the number of potential arrangements from millions to mere hundreds.
"We divided 32 into the short, middle and long (permutations)," said Zeng, who helped develop the divide-and-protect approach in 2008. "We lined up all those possible arrangements, and then we computed their energies to find the most stable ones.
"Without those rules, it's like finding a needle in the Platte River. With them, it's like finding a needle in the fountain outside the Nebraska Union. It's still hard, but it's much more manageable. You have a much narrower range."
The researchers resorted to the computational approach because of the difficulty of capturing the structure via X-ray crystallography or single-particle transmission electron microscopy, two of the most common imaging methods at the atomic scale.
Knowing the nanoparticle's most stable configurations, Zeng said, could allow biomedical engineers to identify appropriate binding sites for drugs used to treat cancer and other diseases. The findings could also optimize the use of gold nanoparticles in catalyzing the oxidation process that transforms dangerous carbon monoxide emissions into the less noxious carbon dioxide, he said.
###
Zeng and Gao co-authored the study with Wen Wu Xu, who works with Gao at the Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics. The team, which received support from the U.S. Army Research Laboratory and UNL's Nebraska Center for Energy Sciences Research, performed most of its computational analyses through the Holland Computing Center.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Xiao Cheng Zeng
402-472-9894
Copyright © University of Nebraska-Lincoln
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Chemistry
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Environment
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
![]() SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Industrial
![]() Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
![]() Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
![]() Nanotubes: a promising solution for advanced rubber cables with 60% less conductive filler June 1st, 2022
Nanotubes: a promising solution for advanced rubber cables with 60% less conductive filler June 1st, 2022
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








