Home > Press > Scientists create new atomic X-ray laser
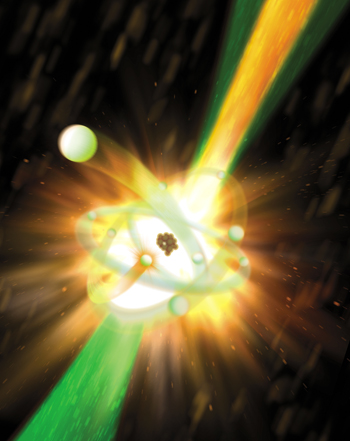 |
| A powerful X-ray laser pulse from SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory's Linac Coherent Light Source comes up from the lower-left corner (green) and hits a neon atom (center). Illustration by Gregory M. Stewart/SLAC |
Abstract:
Lab scientists and international collaborators have created the shortest, purest X-ray laser pulses ever achieved, fulfilling a 45-year-old prediction and ultimately opening the door to new medicines, devices and materials.
Scientists create new atomic X-ray laser
Livermore, CA | Posted on January 26th, 2012The researchers, reporting today (Jan. 26) in Nature, aimed radiation from the Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS), located at the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center (SLAC), at a cell containing neon gas, setting off an avalanche of X-ray emissions to create a new "atomic X-ray laser."
"X-rays give us a penetrating view into the world of atoms and molecules," said physicist Nina Rohringer, a former LLNL postdoc, now a group leader at Max Planck Society's Advanced Study Group. She collaborated with researchers from SLAC, LLNL and Colorado State University.
Livermore scientists include Rich London, Felice Albert, Jim Dunn, Alex Graf, Randy Hill and Stefan Hau-Riege.
The new laser fulfills a 1967 prediction, which proposed that X-ray lasers could be made by first removing inner electrons from atoms and then inducing electrons to fall from higher to lower energy levels, releasing a single color of light in the process. But until 2009, when LCLS turned on, no X-ray sources were powerful enough to create this type of laser.
To make the atomic X-ray laser, LCLS's powerful X-ray pulses -- each a billion times brighter than any available before -- knocked electrons out of the inner shells of many of the neon atoms. When other electrons fell in to fill the holes, about one in 50 atoms responded by emitting a so-called hard X-ray, which has a very short wavelength. Those X-rays then stimulated neighboring neon atoms to emit more X-rays, creating a domino effect that amplified the laser light 200 million times.
"This work presents a big advance in the quest for shorter wavelength lasers," London said. "In addition, the demonstration of the neon X-ray laser provides a very sensitive test of the physics of intense X-ray interaction with atoms. By comparing theoretical modeling to the observed output signals, one can pin down the basic ultrafast processes occurring in the region where the LCLS beam interacts with the gas."
In the future, Rohringer says she will try to create even shorter-pulse, higher-energy atomic X-ray lasers using oxygen, nitrogen or sulfur gases.
The research was funded by LLNL's Laboratory Research and Development program. LDRD is used to fund creative basic and applied research activities in areas aligned with the Lab's principal missions.
####
About Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
Founded in 1952, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory provides solutions to our nation's most important national security challenges through innovative science, engineering and technology. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory is managed by Lawrence Livermore National Security, LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy's National Nuclear Security Administration.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Anne M Stark
LLNL
(925) 422-9799
Copyright © Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








