Home > Press > Understanding How Cells Respond to Nanoparticles
 |
| Nanoparticles are finding utility in myriad biotechnological applications, including gene regulation, intracellular imaging, and medical diagnostics. Thus, evaluating the biocompatibility of these nanomaterials is imperative. Here we use genome-wide expression profiling to study the biological response of HeLa cells to gold nanoparticles functionalized with nucleic acids. |
Abstract:
Gold nanoparticles are showing real promise as vehicles for efficiently delivering therapeutic nucleic acids, such as disease-fighting genes and small interfering RNA (siRNA) molecules, to tumors. Now, a team of investigators from Northwestern University has shown that the safety of gold nanoparticle-nucleic acid formulations depends significantly on how the nucleic acids and nanoparticles are linked to one another, a finding with important implications for those researchers developing such constructs.
Understanding How Cells Respond to Nanoparticles
Bethesda, MD | Posted on October 27th, 2010Chad Mirkin, co-principal investigator of the Northwestern University Center for Cancer Nanotechnology Excellence, one of nice such centers established by the National Cancer Institute (NCI), led the team of investigators that studied how cells respond to different nucleic acid-nanoparticle formulations. The investigators published their results in the journal ACS Nano.
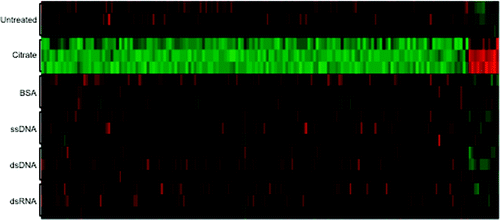
To measure how cancer cells respond when they take up nanoparticles, Dr. Mirkin and his colleagues used a technique known as genome-wide expression profiling, which measures relative changes in global gene expression. The investigators added different types of nanoparticles to cancer cells growing in culture dishes and then obtained whole genome expression profiles for the cells. In all the experiments, the researchers attached non-targeting nucleic acids attached to the nanoparticles in order to minimize gene changes that might be triggered through a therapeutic effect relating to a specific, designed interaction between the nucleic acid and a targeted gene.
The results of these comparison studies showed that the surface properties of the nanoparticles had a profound impact on how a given nanoparticle impacts gene expression within a cell. The researchers observed the most surprising and noteworthy difference when they compared two nanoparticles that differed only in the manner in which the nucleic acids were attached to the nanoparticle surface. Nanoparticles loosely linked to the nucleic acids triggered large-scale changes in gene expression, while in contrast, nanoparticles linked tightly to nucleic acids through a covalent chemical bond had virtually no effect on gene expression. These findings, the researchers noted, show how important it is to fully characterize nanoparticles not only in terms of the shape and size, but also with respect to their surface properties.
This work, which is detailed in a paper titled, "Cellular Response of Polyvalent Oligonucleotide-Gold Nanoparticle Conjugates," was supported in part by the NCI Alliance for Nanotechnology in Cancer, a comprehensive initiative designed to accelerate the application of nanotechnology to the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of cancer. An abstract of this paper is available at the journal's website.
View abstract at pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/nn102228s
####
About NCI Alliance for Nanotechnology in Cancer
To help meet the goal of reducing the burden of cancer, the National Cancer Institute (NCI), part of the National Institutes of Health, is engaged in efforts to harness the power of nanotechnology to radically change the way we diagnose, treat and prevent cancer.
The NCI Alliance for Nanotechnology in Cancer is a comprehensive, systematized initiative encompassing the public and private sectors, designed to accelerate the application of the best capabilities of nanotechnology to cancer.
Currently, scientists are limited in their ability to turn promising molecular discoveries into benefits for cancer patients. Nanotechnology can provide the technical power and tools that will enable those developing new diagnostics, therapeutics, and preventives to keep pace with today’s explosion in knowledge.
For more information, please click here
Copyright © NCI Alliance for Nanotechnology in Cancer
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








