Home > Press > Super cool atom thermometer
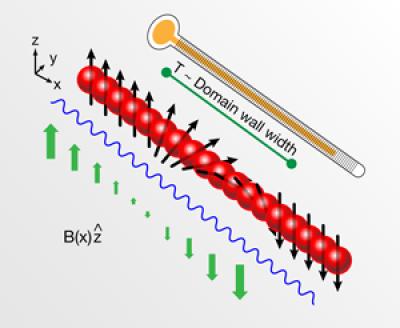 |
| Physicists have developed a new thermometry method suitable for measuring temperatures of ultracold atoms. Credit: Illustration: Alan Stonebraker |
Abstract:
Physicists face the daunting task of developing new, reliable ways of measuring extreme low temperatures.
Super cool atom thermometer
College Park, MD | Posted on December 9th, 2009As physicists strive to cool atoms down to ever more frigid temperatures, they face the daunting task of developing new, reliable ways of measuring these extreme lows. Now a team of physicists has devised a thermometer that can potentially measure temperatures as low as tens of trillionths of a degree above absolute zero. Their experiment is reported in the current issue of Physical Review Letters and highlighted with a Viewpoint in the December 7 issue of Physics (physics.aps.org.)
Physicists can currently cool atoms to a few billionths of a degree, but even this is too hot for certain applications. For example, Richard Feynman dreamed of using ultracold atoms to simulate the complex quantum mechanical behavior of electrons in certain materials. This would require the atoms to be lowered to temperatures at least a hundred times colder than what has ever been achieved. Unfortunately, thermometers that can measure temperatures of a few billionths of a degree rely on physics that doesn't apply at these extremely low temperatures.
Now a team at the MIT-Harvard Center for Ultra-Cold Atoms has developed a thermometer that can work in this unprecedentedly cold regime. The trick is to place the system in a magnetic field, and then measure the atoms' average magnetization. By determining a handful of easily-measured properties, the physicists extracted the temperature of the system from the magnetization. While they demonstrated the method on atoms cooled to one billionth of a degree, they also showed that it should work for atoms hundreds of times cooler, meaning the thermometer will be an invaluable tool for physicists pushing the cold frontier.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
James Riordon
301-209-3238
Copyright © Eurekalert
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








