Home > Press > AFOSR's basic research may lead to revolutionary new devices
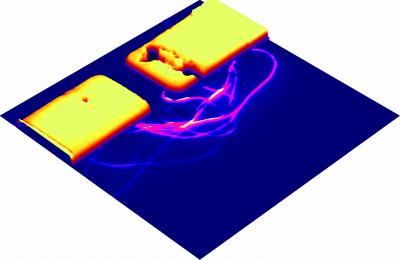 |
| Dr. Jiwoong Park of Cornell University, who receives basic research funding from the Air Force Office of Scientific Research is investigating carbon nanostructures that may someday be used in electronic, thermal, mechanical and sensing devices for the Air Force.
Credit: Credit: Adam Tsen, Cornell University |
Abstract:
Dr. Jiwoong Park of Cornell University, who receives funding for basic research from the Air Force Office of Scientific Research (AFOSR), is investigating carbon nanostructures that may some day be used in electronic, thermal, mechanical and sensing devices for the Air Force.
"Devices that are required in many of the Air Force missions are somewhat different from commercial ones in the sense that they are often exposed to harsh environments while maintaining their maximum performance," Park said. "Carbon-based nanostructures, including carbon nanotubes and graphenes (thin layers of graphite) present many exciting properties that may lead to new device structures."
AFOSR's basic research may lead to revolutionary new devices
USA | Posted on September 25th, 2009Park's team of researchers is examining single molecules, nanocrystals, nanowires, carbon nanotubes and their arrays in an effort to find a "bridging" material that has a stable structure for making molecular-level bonds. In addition, they are seeking an effective tool for resolving functional and structural challenges. If successful, they will be able to apply the research to future technological advances.
Park's research may contribute to the discovery of new electronic and optical devices that will revolutionize electrical engineering and bioengineering as well as physical and materials science.
As a result of Park's highly innovative work, the U.S. government has selected him to be a 2008 PECASE (Presidential Early Career Award in Science and Engineering) Award winner. The prestigious and much sought after award is the highest honor the government presents to promising scientists and engineers at the beginning of their careers. Each award winner receives a citation, a plaque, and up to $1 million in funding from the nominating agency (AFOSR).
"I fully expect that over the five-year period of the PECASE award, Professor Park will have established himself as a world leader in carbon nanotube and graphene research," said Dr. Harold Weinstock, the AFOSR program manager responsible for nominating Park.
####
About Air Force Office of Scientific Research
The Air Force Office of Scientific Research (AFOSR), located in Arlington, Virginia, continues to expand the horizon of scientific knowledge through its leadership and management of the Air Force's basic research program. As a vital component of the Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL), AFOSR's mission is to discover, shape, and champion basic science that profoundly impacts the future Air Force.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Maria Callier
703-696-7308
Copyright © Air Force Office of Scientific Research
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








