Home > Press > Computer simulations shed light on nanosized minerals
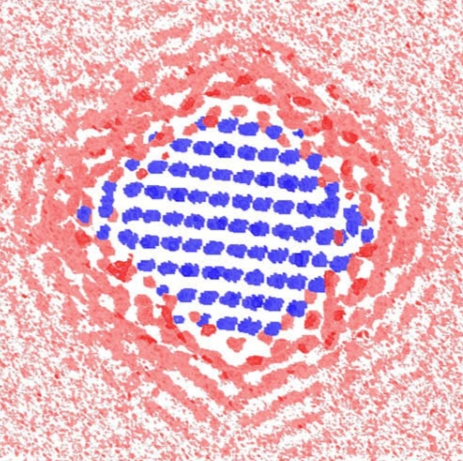 |
| Why nanosized minerals do what they do: This computer simulation reveals the cross section of the water density around a 2.7 nanometer faceted particle. The blue indicates an iron site, pink indicates the area with low water density, and red indicates the area with high water density. |
Abstract:
The red and blue images appear ghostly, like a fleeting glimpse of something that's never been seen before — which is true. Using computer simulations, Berkeley Lab scientists have developed the first predicted images of water molecules surrounding a nanoparticle, in this case an iron-oxide mineral called hematite.
Computer simulations shed light on nanosized minerals
Berkeley, CA | Posted on July 6th, 2009The simulations indicate that the size and shape of the nanosized mineral determines the way in which water molecules layer around it. And this influences how the mineral interacts with its environment, including other nanoparticles, dissolved ions, and the surfaces of larger minerals and bacteria.
The images are a peek into the hidden world of nanosized minerals, which are important components of geochemical cycles in soils, groundwater, rivers and lakes. They're also key players in some of the biggest challenges facing scientists today. Cleaning up contaminants left over from abandoned mines, or learning how to store carbon underground — where it can't contribute to climate change — will require a better understanding of how nanosized minerals participate in these processes.
Addressing these headline-grabbing problems is one of the reasons behind the recently created Berkeley Nanogeoscience Center, located at Berkeley Lab, which seeks to uncover the roles played by nanosized particles in geochemical processes — both manmade and natural. The multidisciplinary group of scientists utilizes cutting edge imaging technologies and computer simulations to learn what makes nanosized minerals tick.
Consider subsurface contaminants. In California, decades of mining activity have yielded large quantities of toxic metal ions that threaten to leach into watersheds. These ions are often adsorbed onto mineral nanoparticles.
"To understand how such contaminants move, we have to understand how nanoparticles move through the subsurface, carrying with them metal ions that are sorbed onto their surface," says Jill Banfield, a principal investigator in the Geochemistry Department of Berkeley Lab's Earth Sciences Division, and a UC Berkeley professor in the Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences and in the Department of Environmental Science, Policy and Management.
There's one problem, however. Nanosized minerals abide by their own, often poorly understood rules. At the nanoscale, which is smaller than 100 nanometers in diameter (one nanometer is one-billionth of a meter), a mineral is more surface than volume. And this can change the way it reacts in unexpected ways.
To explore this world, scientists at the Berkeley Nanogeoscience Center utilize transmission electron microscopy at Berkeley Lab's National Center for Electron Microscopy, which offers extremely high-resolution imaging. Berkeley Lab's Advanced Light Source, a national user facility that generates intense light for scientific research, is used to characterize the chemistry of nanoparticles and image their association with biopolymers and cells.
In their most recent work, the scientists used a dedicated computing cluster that's tailored for nanogeoscience research. Dino Spagnoli, working with a team of scientists from Berkeley Lab's Earth Sciences Division, performed molecular dynamics simulations of different shapes and sizes of a hematite nanoparticle to investigate how water molecules surround it.
"Based on the shape and size of the nanoparticle, and how water surrounds it, we can predict how ions will adsorb to the surface, which is essential to understanding crystal growth," says Spagnoli, who is now with the Curtin University of Technology in Australia.
The simulations predict that water molecules enshroud nanoparticles in ordered layers that change their organization with particle size and shape. With larger faceted nanoparticles, water molecules at the corners are less layered. This makes it easier for an ion to swim to the nanoparticle's surface. In contrast, water molecules become trapped around spherical nanoparticles, decreasing ion mobility.
"It is much easier for compounds to get to the surface of a faceted rather than a spherical particle," adds Banfield. "Overall, we found that water behaves differently based on size and shape of the nanoparticle, and this influences how it reacts with other minerals."
"Prediction of the effects of size and morphology on the structure of water around hematite nanoparticles" by Dino Spagnoli, Benjamin Gilbert, Glenn Waychunas, and Jillian Banfield appears in a recent issue of the journal Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. The paper was featured in the Editor's Choice section of the May 22, 2009 issue of Science. This research was funded by the Department of Energy.
####
About Berkeley Lab
In the world of science, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) is synonymous with “excellence.” Eleven scientists associated with Berkeley Lab have won the Nobel Prize and 55 Nobel Laureates either trained here or had significant collaborations with our Laboratory. Thirteen of our scientists have won the National Medal of Science, our nation's highest award for lifetime achievement in fields of scientific research. As of 2008, there have been 61 Berkeley Lab scientists elected into the National Academy of Sciences (NAS), considered one of the highest honors for a scientist in the United States. This translates to approximately three-percent of the total NAS membership, an unparalleled record of achievement. Eighteen of our engineers have been elected to the National Academy of Engineering, and two of our scientists have been elected into the Institute of Medicine. In addition, Berkeley Lab has trained thousands of university science and engineering students who are advancing technological innovations across the nation and around the world.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dan Krotz
(510) 486-4019
Copyright © Berkeley Lab
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Berkeley Nanogeoscience Center
Berkeley Nanogeoscience Center
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








