Home > Press > New Technique Reveals Hidden Properties of Ultracold Atomic Gases
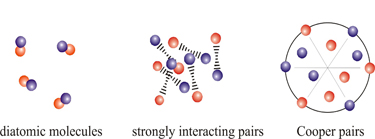 |
| A powerful new JILA technique reveals hidden properties of ultracold atoms in a superfluid, in which atoms form pairs like electrons in a superconductor. The JILA group focuses on the "crossover" stage (middle graphic) between the small pairs of a Bose-Einstein Condensate (left) and the extremely large pairs of a low-temperature superconductor (right).
Credit: C. Regal/JILA |
Abstract:
Physicists at JILA, a joint institute of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the University of Colorado at Boulder, have demonstrated a powerful new technique that reveals hidden properties of ultracold atomic gases.
New Technique Reveals Hidden Properties of Ultracold Atomic Gases
GAITHERSBURG, MD | Posted on August 6th, 2008To develop the new technique, the scientists borrowed an idea used for nearly a century in the study of materials: photoemission spectroscopy. Traditional photoemission spectroscopy probes the energy of electrons in a material. The new photoemission spectroscopy technique, described in the Aug. 7 issue of Nature,* adapts this technique to study potassium atoms in an ultracold gas.
Photoemission spectroscopy is particularly powerful in revealing details of the pairing of electrons in high-temperature superconductors, which are solids that have zero resistance to electrical current at relatively high temperatures (but still below room temperature). The scientists at JILA study a very similar phenomenon: superfluidity (fluids that can flow with zero friction). Specifically, they study how atoms in a Fermi gas behave as they "cross over" from acting like a Bose Einstein Condensate (in which fermions pair up to form tightly bound molecules) to behaving like pairs of separated electrons in a superconductor.
In the crossover region, atoms in an ultracold gas exert very strong forces on each other, which masks their individual properties. To see the hidden behavior, JILA scientists apply a radio frequency field to a cloud of trapped, paired potassium atoms, ejecting a few atoms from the strongly interacting cloud. Then the laser trap is turned off so the gas can expand. Scientists make images and count the numbers of escaping atoms at different velocities. With this information, scientists can calculate the atoms' original energy states and momentum values back when they were inside the gas. Scientists then map the energy levels for all the original states of the atoms and can identify a particular pattern that shows the appearance of a large "energy gap," which represents the amount of energy needed to break apart a pair of atoms.
The new photoemission technique represents a huge jump in the information available to physicists who study ultracold gases. Traditionally, scientists could probe either the energy or momentum of these gases, not both. The new technique simultaneously probes the energy and momentum, allowing the scientists to study the microscopics involved in the pairing of two atoms.
"This technique is a clean probe of the microscopics in this system, and it allows us to see interesting things like a very large energy gap that seems to appear before the superfluid state," says group leader Deborah Jin, a JILA/NIST fellow. Another research group previously identified what seemed to be an energy gap; however, the results of the JILA technique are much clearer to interpret, Jin says.
Ultimately, the JILA work studying superfluidity in atomic gases may one day help in understanding the energy gap that appears in high-temperature superconductors, which may have applications such as more efficient transmission of electricity across power grids. In addition, the new technique can be extended beyond the study of pairing to include, for example, the study of atoms trapped in crisscrossed "lattices" of laser light, a building block for some atomic clock and quantum computer designs.
Funding for the research was provided by the National Science Foundation.
*J.T. Stewart, J.P. Gaebler and D.S. Jin. Using photoemission spectroscopy to probe a strongly interacting Fermi gas. Nature. Aug. 7, 2008.
####
About NIST
Founded in 1901, NIST is a non-regulatory federal agency within the U.S. Department of Commerce. NIST's mission is to promote U.S. innovation and industrial competitiveness by advancing measurement science, standards, and technology in ways that enhance economic security and improve our quality of life.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Laura Ost
(303) 497-4880
Copyright © NIST
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








