Home > Press > Double-walled nanotubes have electro-optical advantages :Rice University calculations show they could be highly useful for solar panels
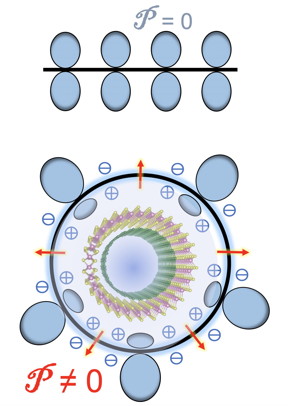 |
| Rice University theorists have calculated flexoelectric effects in double-walled carbon nanotubes. The electrical potential (P) of atoms on either side of a graphene sheet (top) are identical, but not when the sheet is curved into a nanotube. Double-walled nanotubes (bottom) show unique effects as band gaps in inner and outer tubes are staggered. (Credit: Yakobson Research Group/Rice University) |
Abstract:
One nanotube could be great for electronics applications, but there’s new evidence that two could be tops.
Double-walled nanotubes have electro-optical advantages :Rice University calculations show they could be highly useful for solar panels
Houston, TX | Posted on March 27th, 2020Rice University engineers already knew that size matters when using single-walled carbon nanotubes for their electrical properties. But until now, nobody had studied how electrons act when confronted with the Russian doll-like structure of multiwalled tubes.
The Rice lab of materials theorist Boris Yakobson has now calculated the impact of curvature of semiconducting double-wall carbon nanotubes on their flexoelectric voltage, a measure of electrical imbalance between the nanotube’s inner and outer walls.
This affects how suitable nested nanotube pairs may be for nanoelectronics applications, especially photovoltaics.
The theoretical research by Yakobson’s Brown School of Engineering group appears in the American Chemical Society journal Nano Letters.
In an 2002 study, Yakobson and his Rice colleagues had revealed how charge transfer, the difference between positive and negative poles that allows voltage to exist between one and the other, scales linearly to the curvature of the nanotube wall. The width of the tube dictates curvature, and the lab found that the thinner the nanotube (and thus larger the curvature), the greater the potential voltage.
When carbon atoms form flat graphene, the charge density of the atoms on either side of the plane are identical, Yakobson said. Curving the graphene sheet into a tube breaks that symmetry, changing the balance.
That creates a flexoelectric local dipole in the direction of, and proportional to, the curvature, according to the researchers, who noted that the flexoelectricity of 2D carbon “is a remarkable but also fairly subtle effect.”
But more than one wall greatly complicates the balance, altering the distribution of electrons. In double-walled nanotubes, the curvature of the inner and outer tubes differ, giving each a distinct band gap. Additionally, the models showed the flexoelectric voltage of the outer wall shifts the band gap of the inner wall, creating a staggered band alignment in the nested system.
“The novelty is that the inserted tube, the ‘baby’ (inside) matryoshka has all of its quantum energy levels shifted because of the voltage created by exterior nanotube,” Yakobson said. The interplay of different curvatures, he said, causes a straddling-to-staggered band gap transition that takes place at an estimated critical diameter of about 2.4 nanometers.
“This is a huge advantage for solar cells, essentially a prerequisite for separating positive and negative charges to create a current,” Yakobson said. “When light is absorbed, an electron always jumps from the top of an occupied valence band (leaving a ‘plus’ hole behind) to the lowest state of the empty conductance band.
“But in a staggered configuration they happen to be in different tubes, or layers,” he said. “The ‘plus’ and ‘minus’ get separated between the tubes and can flow away by generating current in a circuit.”
The team’s calculations also showed that modifying the nanotubes’ surfaces with either positive or negative atoms could create “substantial voltages of either sign” up to three volts. “Although functionalization could strongly perturb the electronic properties of nanotubes, it may be a very powerful way of inducing voltage for certain applications,” the researchers wrote.
The team suggested its findings may apply to other types of nanotubes, including boron nitride and molybdenum disulfide, on their own or as hybrids with carbon nanotubes.
Rice alumnus Vasilii Artyukhov, now at Quantlab Financial, Houston, is lead author of the paper. Co-authors are Rice graduate student Sunny Gupta and research scientist Alex Kutana. Yakobson is the Karl F. Hasselmann Professor of Materials Science and NanoEngineering and a professor of chemistry at Rice.
The Army Research Office and the Robert Welch Foundation supported the research, with computational support from the Department of Defense High Performance Computing Modernization Program and the Department of Energy Office of Science.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation’s top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,962 undergraduates and 3,027 graduate students, Rice’s undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is just under 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for lots of race/class interaction and No. 4 for quality of life by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger’s Personal Finance.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jeff Falk
713-348-6775
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Curvature-induced polarization in carbon nanoshells:
Curvature-induced polarization in carbon nanoshells:
![]() Rice Department of Materials Science and Nanoengineering:
Rice Department of Materials Science and Nanoengineering:
![]() George R. Brown School of Engineering:
George R. Brown School of Engineering:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
![]() Physicists unlock the secret of elusive quantum negative entanglement entropy using simple classical hardware August 16th, 2024
Physicists unlock the secret of elusive quantum negative entanglement entropy using simple classical hardware August 16th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








