Home > Press > Ultra-small nanoprobes could be a leap forward in human-machine interfaces
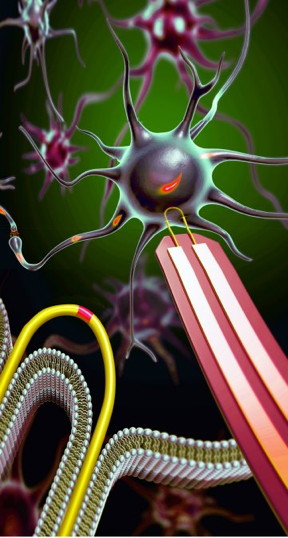 |
| U-shaped nanowires can record electrical chatter inside a brain or heart cell without causing any damage. The devices are 100 times smaller than their biggest competitors, which kill a cell after recording. Credit: Lieber Group, Harvard University |
Abstract:
Machine enhanced humans - or cyborgs as they are known in science fiction - could be one step closer to becoming a reality, thanks to new research from the University of Surrey and Harvard University.
Ultra-small nanoprobes could be a leap forward in human-machine interfaces
Guildford, UK | Posted on July 4th, 2019Researchers have conquered the monumental task of manufacturing scalable nanoprobe arrays small enough to record the inner workings of human cardiac cells and primary neurons.
The ability to read electrical activities from cells is the foundation of many biomedical procedures, such as brain activity mapping and neural prosthetics. Developing new tools for intracellular electrophysiology (the electric current running within cells) that push the limits of what is physically possible (spatiotemporal resolution) while reducing invasiveness could provide a deeper understanding of electrogenic cells and their networks in tissues, as well as new directions for human-machine interfaces.
In a paper published by Nature Nanotechnology, scientists from Surrey's Advanced Technology Institute (ATI) and Harvard University detail how they produced an array of the ultra-small U-shaped nanowire field-effect transistor probes for intracellular recording. This incredibly small structure was used to record, with great clarity, the inner activity of primary neurons and other electrogenic cells, and the device has the capacity for multi-channel recordings.
Dr Yunlong Zhao from the ATI at the University of Surrey said: "If our medical professionals are to continue to understand our physical condition better and help us live longer, it is important that we continue to push the boundaries of modern science in order to give them the best possible tools to do their jobs. For this to be possible, an intersection between humans and machines is inevitable.
"Our ultra-small, flexible, nanowire probes could be a very powerful tool as they can measure intracellular signals with amplitudes comparable with those measured with patch clamp techniques; with the advantage of the device being scalable, it causes less discomfort and no fatal damage to the cell (cytosol dilation). Through this work, we found clear evidence for how both size and curvature affect device internalisation and intracellular recording signal."
Professor Charles Lieber from the Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology at Harvard University said: "This work represents a major step towards tackling the general problem of integrating 'synthesized' nanoscale building blocks into chip and wafer scale arrays, and thereby allowing us to address the long-standing challenge of scalable intracellular recording.
"The beauty of science to many, ourselves included, is having such challenges to drive hypotheses and future work. In the longer term, we see these probe developments adding to our capabilities that ultimately drive advanced high-resolution brain-machine interfaces and perhaps eventually bringing cyborgs to reality."
Professor Ravi Silva, Director of the ATI at the University of Surrey, said: "This incredibly exciting and ambitious piece of work illustrates the value of academic collaboration. Along with the possibility of upgrading the tools we use to monitor cells, this work has laid the foundations for machine and human interfaces that could improve lives across the world."
Dr Yunlong Zhao and his team are currently working on novel energy storage devices, electrochemical probing, bioelectronic devices, sensors and 3D soft electronic systems. Undergraduate, graduate and postdoc students with backgrounds in energy storage, electrochemistry, nanofabrication, bioelectronics, tissue engineering are very welcome to contact Dr Zhao to explore the opportunities further.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dalitso Njolinjo
Copyright © University of Surrey
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() https://www.nature.com/articles/s41565-019-0478-y:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41565-019-0478-y:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Brain-Computer Interfaces
![]() Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
![]() New brain-like computing device simulates human learning: Researchers conditioned device to learn by association, like Pavlov's dog April 30th, 2021
New brain-like computing device simulates human learning: Researchers conditioned device to learn by association, like Pavlov's dog April 30th, 2021
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








