Home > Press > Development of dendritic-network-implementable artificial neurofiber transistors: Transistors with a fibrous architecture similar to those of neurons are capable of forming artificial neural networks. Fibrous networks can be used in smart wearable devices and robots
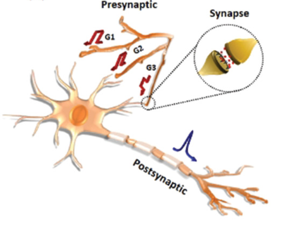 |
| Schematic of biological presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons and a synapse (inset) CREDIT Korea Institute of Science and Technology(KIST) |
Abstract:
Advances in artificial intelligence (AI)-based technologies have led to an astronomical increase in the amounts of data available for processing by computers. Existing computing methods often process data sequentially and therefore have large time and power requirements for processing massive quantities of information. Hence, a transition to a new computing paradigm is required to solve such challenging issues. Researchers are currently working towards developing energy-efficient neuromorphic computing technologies and hardware that are capable of processing massive amounts of information by mimicking the structure and mechanisms of the human brain.
Development of dendritic-network-implementable artificial neurofiber transistors: Transistors with a fibrous architecture similar to those of neurons are capable of forming artificial neural networks. Fibrous networks can be used in smart wearable devices and robots
Sejong, Korea | Posted on September 24th, 2021The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) has reported that a research team led by Dr. Jung ah Lim and Dr. Hyunsu Ju of the Center for Opto-electronic Materials and Devices has successfully developed organic neurofiber transistors with an architecture and functions similar to those of neurons in the human brain, which can be used as a neural network. Research on devices that can function as neurons and synapses is needed so that large-scale computations can be performed in a manner similar to data processing in the human brain. Unlike previously developed devices that act as either neurons or synapses, the artificial neurofiber transistors developed at KIST can mimic the behaviors of both neurons and synapses. By connecting the transistors in arrays, one can easily create a structure similar to a neural network.
Biological neurons have fibrous branches that can receive multiple stimuli simultaneously, and signal transmissions are mediated by ion migrations stimulated by electrical signals. The KIST researchers developed the aforementioned artificial neurofibers using fibrous transistors previously developed by them in 2019. They devised memory transistors that remember the strengths of the applied electrical signals, similar to synapses, and transmit them via redox reactions between the semiconductor channels and ions within the insulators upon receiving the electrical stimuli from the neurofiber transistors. These artificialneurofibers also mimic the signal summation functionality of neurons.
The researchers created an artificial neural network system comprising 100 synapses using the artificial neurofibers and verified the stability of the device via speech recognition experiments. The proposed neural network was shown to achieve a recognition accuracy of 88.9% after training with speech data.
Dr. Jung Ah Lim and Dr. Hyunsu Ju note that "the novel artificial neurofiber device is an original technology that can be used to create large-scale, energy-efficient (~2 pJ/signal), and highly reliable artificial neural networks similar to that of the brain. Our artificial neurofiber device is flexible and may be used in AI-enabled wearable electronics made of semiconductor materials or in robotics."
####
About National Research Council of Science & Technology
The Korea Institute of Science and Technology(KIST). Founded as the first multidisciplinary government-funded research institute in Korea, KIST established a national development strategy based on science and technology and disseminated various essential industrial technologies. Now, half a century later, KIST is elevating Korea's status in the field of science and technology through world-leading fundamental technology R&D. Looking to the future, KIST will continue to strive to be a premier research institute, pursuing a brighter future for Korea and all of humanity.
The research was backed by the Ministry of Science and ICT and conducted as part of a institutional research program of KIST and the National Research Foundation of Korea’s mid-career Researcher Program. This study has been published in the latest issue of Advanced Materials (IF : 27.34, JCR top 1.61%).
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Young Mi Kim
National Research Council of Science & Technology
Office: 82-442-877-376
Expert Contacts
Dr. Lim, Jung Ah
Korea Institute of Science and Technology
Office: +82-2-958-5378
Kim, Dohyun (PR Department)
Korea Institute of Science and Technology
Office: +82-2-958-6344
Copyright © National Research Council of Science & Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Brain-Computer Interfaces
![]() Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
![]() New brain-like computing device simulates human learning: Researchers conditioned device to learn by association, like Pavlov's dog April 30th, 2021
New brain-like computing device simulates human learning: Researchers conditioned device to learn by association, like Pavlov's dog April 30th, 2021
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Artificial Intelligence
![]() New quantum encoding methods slash circuit complexity in machine learning November 8th, 2024
New quantum encoding methods slash circuit complexity in machine learning November 8th, 2024
![]() Rice research could make weird AI images a thing of the past: New diffusion model approach solves the aspect ratio problem September 13th, 2024
Rice research could make weird AI images a thing of the past: New diffusion model approach solves the aspect ratio problem September 13th, 2024
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








