Home > Press > Zips on the nanoscale: New method of synthesising nanographene on metal oxide surfaces
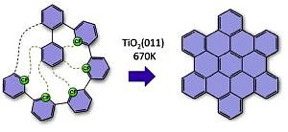 |
| The desired nanographenes form like dominoes via cyclodehydrofluorination on the titanium oxide surface. All ‘missing’ carbon-carbon bonds are thus formed after each other in a formation that resembles a zip being closed. (Image: FAU/Konstantin Amsharov) |
Abstract:
Nanostructures based on carbon are promising materials for nanoelectronics. However, to be suitable, they would often need to be formed on non-metallic surfaces, which has been a challenge - up to now. Researchers at Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU) have found a method of forming nanographenes on metal oxide surfaces. Their research, conducted within the framework of collaborative research centre 953 - Synthetic Carbon Allotropes funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG), has now been published in the journal Science.
Zips on the nanoscale: New method of synthesising nanographene on metal oxide surfaces
Nuremberg, Germany | Posted on March 5th, 2019Two-dimensional, flexible, tear-resistant, lightweight, and versatile are all properties that apply to graphene, which is often described as a miracle material. In addition, this carbon-based nanostructure has unique electrical properties that make it attractive for nanoelectronic applications. Depending on its size and shape, nanographene can be conductive or semi-conductive - properties that are essential for use in nanotransistors. Thanks to its good electrical and thermal conductivity, it could also replace copper (which is conductive) and silicon (which is semi-conductive) in future nanoprocessors.
New: Nanographene on metal oxides
The problem: In order to create an electronic circuit, the molecules of nanographene must be synthesised and assembled directly on an insulating or semi-conductive surface. Although metal oxides are the best materials for this purpose, in contrast to metal surfaces, direct synthesis of nanographenes on metal oxide surfaces is not possible as they are considerably less chemically reactive. The researchers would have to carry out the process at high temperatures, which would lead to several uncontrollable secondary reactions. A team of scientists led by Dr. Konstantin Amsharov from the Chair of Organic Chemistry II have now developed a method of synthesising nanographenes on non-metallic surfaces, that is insulating surfaces or semi-conductors.
It's all about the bond
The researchers' method involves using a carbon fluorine bond, which is the strongest carbon bond. It is used to trigger a multilevel process. The desired nanographenes form like dominoes via cyclodehydrofluorination on the titanium oxide surface. All 'missing' carbon-carbon bonds are thus formed after each other in a formation that resembles a zip being closed. This enables the researchers to create nanographenes on titanium oxide, a semi-conductor. This method also allows them to define the shape of the nanographene by modifying the arrangement of the preliminary molecules. New carbon-carbon bonds and, ultimately, nanographenes form where the researchers place the fluourine atoms. For the first time, these research results demonstrate how carbon-based nanostructures can be manufactured by direct synthesis on the surfaces of technically-relevant semi-conducting or insulating surfaces. 'This groundbreaking innovation offers effective and simple access to electronic nanocircuits that really work, which could scale down existing microelectronics to the nanometre scale,' explains Dr. Amsharov.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Konstantin Amsharov
49-913-185-65507
Copyright © Zips on the nanoscale New method of synthesising nanographene on metal oxide surfaces
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
2 Dimensional Materials
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Chip Technology
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Nanoelectronics
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
![]() Atomic level deposition to extend Moore’s law and beyond July 15th, 2022
Atomic level deposition to extend Moore’s law and beyond July 15th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Industrial
![]() Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
![]() Nanotubes: a promising solution for advanced rubber cables with 60% less conductive filler June 1st, 2022
Nanotubes: a promising solution for advanced rubber cables with 60% less conductive filler June 1st, 2022
![]() Protective equipment with graphene nanotubes meets the strictest ESD safety standards March 25th, 2022
Protective equipment with graphene nanotubes meets the strictest ESD safety standards March 25th, 2022
![]() OCSiAl receives the green light for Luxembourg graphene nanotube facility project to power the next generation of electric vehicles in Europe March 4th, 2022
OCSiAl receives the green light for Luxembourg graphene nanotube facility project to power the next generation of electric vehicles in Europe March 4th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








