Home > Press > Flipping the switch on supramolecular electronics
 |
| This is a photo-switchable molecular crystals in two dimensions. CREDIT Nature Publishing Group |
Abstract:
•Partners of the European Project 'Graphene Flagship' at the University of Strasbourg and CNRS (France), together with an international team of collaborators, created new 'switches' that respond to light.
•Researchers combined light-sensitive molecules with layers graphene and other 2D materials to create new devices that could be used in sensors, optoelectronics and flexible devices.
•The study, recently published in Nature Communications, may lead to a variety of programmable applications in the next generations of smart electronics.
Flipping the switch on supramolecular electronics
Cambridge, UK | Posted on August 14th, 2018Graphene and related materials hold great potential for technological applications such as electronics, sensors, and energy storage devices, among others. Thanks to their high surface sensitivity, these materials are an ideal platform to study the interplay between molecular assemblies at the nanoscale and macroscopic electrical phenomena.
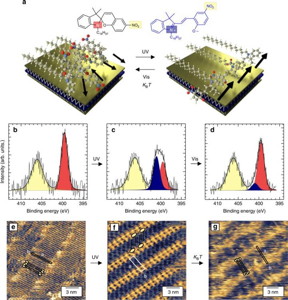
Researchers within the Graphene Flagship designed a molecule that can reversibly undergo chemical transformations when illuminated with ultraviolet and visible light. This molecule -a photoswitchable spiropyran- can be then anchored to the surface of materials such as graphene or molybdenum disulfide, thus generating an atomically precise hybrid macroscopic superlattice. When illuminated, the whole supramolecular structure experiences a collective structural rearrangement, which could be directly visualized with a sub-nanometer resolution by scanning tunneling microscopy.
More importantly, this light-induced reorganization at the molecular level induces large changes in the macroscopic electrical properties of the hybrid devices. The molecules, together with the layers of graphene and related materials, can convert single-molecule events into a spatially homogeneous switching action that generates a macroscopic electrical response. This novel and versatile approach takes supramolecular electronics to the next level.
'Thanks to this new approach, we can exploit the capacity of collective switching events occurring in superlattices of photochromic molecules assembled onto graphene and related materials to induce large scale and reversible modulation in the electrical properties of high-performance opto-electronic devices,' explains Paolo Samorì, lead author of the paper. 'This technology could find applications in the next generation of smart and portable electronics, with programmable properties,' he adds.
Samorì also explains how this idea of tailoring molecular superlattices could generate a wide variety of new materials with tunable and responsive properties. 'To dial your functions! You only need to carefully choose the right molecules, the thus-formed superlattice will allow to maximize the change in properties as a response to external inputs,' he says.
Vittorio Pellegrini, researcher at IIT and Division Leader for Energy, Composites, and Production at the Graphene Flagship, highlights how the research is 'unique in the way it combines graphene and other related materials with light-responsive chemical molecules. These macroscopic arrangements are promising platforms for optoelectronics.' Pellegrini points out the outstanding potential of these new findings: 'the molecular ultra-thin coating can be tailored just by synthesizing different molecules.' Moreover, 'this discovery will lead us to the development of devices, as the technique developed by Samorì and his team can be scaled up in reproducible manner,' he added. Samorì agrees: 'The limit in the scalability is the accessibility to ultra-flat and atomically precise graphene and related materials.'
These advances, made possible by the collaborative environment of the Graphene Flagship, could lead to promising applications in sensors, optoelectronics, and flexible devices. Researchers now dream of high-performance multifunctional hybrid devices under control of nature's most abundant and powerful source of energy - light.
Professor Andrea C. Ferrari, Science and Technology Officer of the Graphene Flagship, and Chair of its management panel added: 'Supra-molecular chemistry has been part of the Flagship research since the very beginning. Over the years our partners have improved and developed the techniques that enable to interface molecules with graphene and related materials. We are now witnessing a steady progress towards applications, as shown by this interesting work.'
####
About Graphene Flagship
The Graphene Flagship is one of the largest research initiatives of the European Union. With a budget of €1 billion, it represents a new form of joint, coordinated research initiative on an unprecedented scale. The overall goal of the Graphene Flagship is to take graphene and related materials from the realm of academic laboratories into European society, facilitating economic growth and creating new jobs, in the space of ten years. Through a consortium that combines more than 150 partners, both academic and industrial, the research effort covers the entire value chain, from materials production to components and system integration, and targets several specific goals that exploit the unique properties of graphene and related materials.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Fernando Gomollon-Bel
44-012-237-62391
Copyright © Graphene Flagship
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Chemistry
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
2 Dimensional Materials
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chip Technology
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Nanoelectronics
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
![]() Atomic level deposition to extend Moore’s law and beyond July 15th, 2022
Atomic level deposition to extend Moore’s law and beyond July 15th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








