Home > Press > Development of low-dimensional nanomaterials could revolutionize future technologies
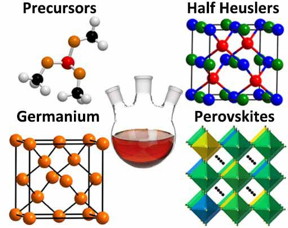 |
| Some of the inorganic semiconductors under study by Vela and coworkers. CREDIT Ames Laboratory |
Abstract:
Javier Vela, scientist at the U.S. Department of Energy's Ames Laboratory, believes improvements in computer processors, TV displays and solar cells will come from scientific advancements in the synthesis of low-dimensional nanomaterials.
Development of low-dimensional nanomaterials could revolutionize future technologies
Ames, IA | Posted on June 15th, 2017Ames Laboratory scientists are known for their expertise in the synthesis and manufacturing of materials of different types, according to Vela, who is also an Iowa State University associate professor of chemistry. In many instances, those new materials are made in bulk form, which means micrometers to centimeters in size. Vela's group is working with tiny, nanometer, or one billionth of a meter sized, nanocrystals.
"We're trying to find out what happens with materials when we go to lower particle sizes, will the materials be enhanced or negatively impacted, or will we find properties that weren't expected," Vela said. "Our goal is to broaden the science of low-dimensional nanomaterials." In an invited paper published in Chemistry of Materials entitled, "Synthetic Development of Low Dimensional Materials", Vela and coauthors Long Men, Miles White, Himashi Andaraarachchi, and Bryan Rosales discussed highlights of some of their most recent work on the synthesis of low dimensional materials.
One of those topics was advancements in the synthesis of germanium-based core-shell nanocrystals. Vela says industry is very interested in semiconducting nanocrystal-based technologies for applications such as solar cells.
Small particle size can affect many things from transport properties (how well a nanocrystal conducts heat and electricity) to optical properties (how strong it interacts with light, absorbs light and emits light). This is especially true in photovoltaic solar cells "Let's say you're using a semiconductor material to make a solar device, there's often different performance when solar cells are made from bulk materials as opposed to when they are made with nanomaterials. Nanomaterials interact with light differently; they absorb it better. That's one way you can manipulate devices and fine tune their performance or power conversion efficiency," said Vela.
Beyond solar cells, Vela says there's tremendous interest in using nanocrystals in quantum dot television and computer displays, optical devices like LEDs (light-emitting diodes), biological imaging, and telecommunications.
He says there are many challenges in this area because depending upon the quality of the nanocrystals used, you can see different emission properties, which can affect the purity of light. "Ultimately the size of the nanocrystals being used can make a huge difference in the cleanliness or crispness of colors in TV and computer displays," said Vela. "Television and computer technology is a multibillion dollar business worldwide, so you can see the potential value our understanding of properties of nanocrystals could bring to these technologies."
In the paper, Vela's group also discussed advancements made in the study of synthesis and spectroscopic characterization of organolead halide perovskites, which Vela says are some of the most promising semiconductors for solar cells because of their low cost and easier processability. He adds photovoltaics made of these materials now reach power conversion efficiencies of greater than 22 percent. Vela's research in this area has focused on mixed-halide perovskites. He says his group has discovered these materials exhibit interesting chemical and photo physical properties that people hadn't realized before, and now they are trying to better understand the correlation between the structure and chemical composition of perovskites and how they behave in solar cells. "One of our goals is to use what we've learned to help lower the cost of solar cells and produce them more reliably and readily," Vela said.
In addition, Vela's group is studying how to replace lead in traditional organolead halide perovskites with something less toxic, like germanium. "In principle, this is an area that should be much better known, but it's not," said Vela. "When we've been able to substitute germanium for lead, we have been able to produce a lighter perovskite, which he says could positively impact the automotive industry, for example.
"This could have great implications for transportation applications where you don't want a lot of lead because it's so heavy," said Vela. Going forward Vela says his group's focus will be on advancing the science in low-dimensional materials.
"We're not working with well-known materials, but the newest; the most recently discovered," Vela said. "And every time we can advance the science we're one step closer to opportunities for more commercialization, more production, more manufacturing and more jobs in the U.S."
###
This work was supported by the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science.
####
About Ames Laboratory
Ames Laboratory is a U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science national laboratory operated by Iowa State University. Ames Laboratory creates innovative materials, technologies and energy solutions. We use our expertise, unique capabilities and interdisciplinary collaborations to solve global problems.
DOE's Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Steve Karsjen
515-294-5643
Copyright © Ames Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Perovskites
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
2 Dimensional Materials
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Laboratories
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Energy
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() Charged “molecular beasts” the basis for new compounds: Researchers at Leipzig University use “aggressive” fragments of molecular ions for chemical synthesis November 3rd, 2023
Charged “molecular beasts” the basis for new compounds: Researchers at Leipzig University use “aggressive” fragments of molecular ions for chemical synthesis November 3rd, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








