Home > Press > Space energy technology restored to make power stations more efficient: Scientists use graphene to reinvent abandoned heat energy converter technology
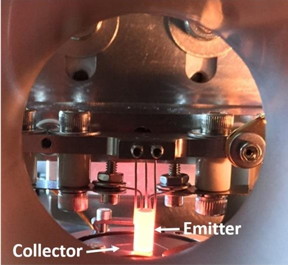 |
| Photograph of the TEC prototype during operation in the Stanford lab. CREDIT © Elsevier |
Abstract:
Satellite-powering technology that was abandoned decades ago has been reinvented to potentially work with traditional power stations to help them convert heat to electricity more efficiently, meaning we would need less fossil fuel to burn for power. A new study in Nano Energy presents a prototype energy converter, which uses graphene instead of metal, making it almost seven times more efficient.
Space energy technology restored to make power stations more efficient: Scientists use graphene to reinvent abandoned heat energy converter technology
Oxford, UK | Posted on March 7th, 2017The researchers behind the study, led by Prof. Roger Howe at Stanford University, say new materials could reignite the field of thermionic energy conversion, improving the way we produce electricity and reducing the impact the process has on the environment.
Energy is one of the most challenging problems society faces today, with an estimated 1.2 billion people having no access to electricity. Thermal energy is one of the most abundant, cheap and widely used energy sources in the world, but it is harvested using old technology: more than 80 percent of the electricity generated in the US comes from mechanical heat engines and turbines based on the 19th century technology that can only be used in large power stations.
Alternatively, the thermionic energy convertor (TEC) can convert heat to electricity more efficiently without the need for big, expensive equipment through the phenomenon of thermionic emission. TECs were first developed in the 1950s for use in space programs, but scientists had not managed to make TECs efficient enough to apply to industrial electricity production. Now, with modern materials and approaches, it is possible to improve their efficiency significantly.
The TEC is composed of two electrodes, namely the emitter and collector, separated by a small vacuum gap. The researchers tested a prototype TEC made using a single sheet of carbon atoms - graphene - instead of tungsten as the collector material. They found the new material improved the efficiency of the TEC, making it 6.7 times more efficient at converting heat into electricity at 1000?C
"TEC technology is very exciting. With improvement in the efficiency, we expect to see an enormous market for it," commented lead author Dr. Hongyuan Yuan from Stanford University. "TECs could not only help make power stations more efficient, and therefore have a lower environmental impact, but they could be also applied in distributed systems like solar cells. In the future, we envisage it being possible to generate 1-2 kW of electricity from water boilers, which could partially power your house."
Existing TEC technology faces two obstacles: a high loss of energy at the anode surface, which leads to reduced output voltage, and high electrical barriers against electrons moving in the gap between the collector and the emitter, which results in reduced output current. For the first time, the new prototype tackles both of these problems simultaneously. The findings of the study reveal an electronic efficiency in energy conversion of 9.8 percent - by far the highest efficiency at 1000?C.
The technology is not yet ready for use in power stations or people's homes - the prototype works in a vacuum chamber but not in a normal setting. The researchers are now working on a vacuum packaged TEC to test the reliability and efficiency of the technology in real applications.
"This prototype is just the first step - there is a lot more to do," said Dr. Yuan. "But our results so far are promising and reflect a happy marriage between modern materials science and an old-fashioned energy technology, which provides a route for re-sparking the field of thermionic energy conversion."
####
About Elsevier
Elsevier is a global information analytics company that helps institutions and professionals progress science, advance healthcare and improve performance for the benefit of humanity. Elsevier provides digital solutions and tools in the areas of strategic research management, R&D performance, clinical decision support, and professional education; including ScienceDirect, Scopus, ClinicalKey and Sherpath. Elsevier publishes over 2,500 digitized journals, including The Lancet and Cell, more than 35,000 e-book titles and many iconic reference works, including Gray's Anatomy. Elsevier is part of RELX Group, a world-leading provider of information and analytics to professionals and business customers, in a wide range of industries. www.elsevier.com
About Nano Energy
Nano Energy is a multidisciplinary, rapid-publication forum of original peer-reviewed contributions on the science and engineering of nanomaterials and nanodevices used in all forms of energy harvesting, conversion, storage, utilization and policy. Through its mixture of articles, reviews, communications, research news, and information on key developments, Nano Energy provides a comprehensive coverage of this exciting and dynamic field which joins nanoscience and nanotechnology with energy science. The journal is relevant to all those who are interested in nanomaterials solutions to the energy problem.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Lucy Rodzynska
44-186-584-3383
Copyright © Elsevier
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Energy
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
Aerospace/Space
![]() Under pressure - space exploration in our time: Advancing space exploration through diverse collaborations and ethical policies February 16th, 2024
Under pressure - space exploration in our time: Advancing space exploration through diverse collaborations and ethical policies February 16th, 2024
![]() Bridging light and electrons January 12th, 2024
Bridging light and electrons January 12th, 2024
![]() Manufacturing advances bring material back in vogue January 20th, 2023
Manufacturing advances bring material back in vogue January 20th, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








