Home > Press > Trickling electrons: Close to absolute zero, the particles exhibit their quantum nature
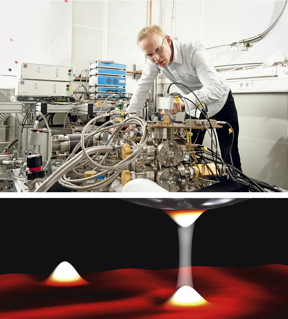 |
| Keeping a close eye on everything: Christian Ast checks the connections of the scanning tunneling microscope (top). Researchers in the Nanoscale Science Department conduct their experiments in this instrument at lowest temperatures of a fifteen thousandth of a degree above absolute zero. The principle is always the same (bottom): A tunneling current (illustrated by the transparent bar) flows between an ultrafine tip and the sample, providing information about the properties of the sample. At these low temperatures the tunneling current reveals all of its quantum properties. CREDIT Tom Pingel (top), MPI for Solid State Research (bottom) |
Abstract:
What would happen if an electric current no longer flowed, but trickled instead? This was the question investigated by researchers working with Christian Ast at the Max Planck Institute for Solid State Research. Their investigation involved cooling their scanning tunnelling microscope down to a fifteen thousandth of a degree above absolute zero. At these extremely low temperatures, the electrons reveal their quantum nature. The electric current is therefore a granular medium, consisting of individual particles. The electrons trickle through a conductor like grains of sand in an hourglass, a phenomenon that can be explained with the aid of quantum electrodynamics.
Trickling electrons: Close to absolute zero, the particles exhibit their quantum nature
Munich, Germany | Posted on November 10th, 2016Flowing water from a tap feels like a homogeneous medium -- it is impossible to distinguish between the individual water molecules. Exactly the same thing is true about electric current. So many electrons flow in a conventional cable that the current appears to be homogeneous. Although it is not possible to distinguish individual electrons, quantum mechanics says they should exist. So how do they behave? Under which conditions does the current not flow like water through a tap, but rather trickles like sand in an hourglass?
The hourglass analogy is very appropriate for the scanning tunnelling microscope, where a thin, pointed tip scans across the surface of a sample without actually touching it. A tiny current flows nevertheless, as there is a slight probability that electrons "tunnel" from the pointed tip into the sample. This tunnelling current is an exponential function of the separation, which is why the pointed tip is located only a few Ångström (a ten millionth of a millimetre) above the sample.
Minute variations in the tunnelling current thus allow researchers to resolve individual atoms and atomic structures on surfaces and investigate their electronic structure. Scanning tunnelling microscopes are therefore some of the most versatile and sensitive detectors in the whole of solid state physics.
Even under these extreme conditions - a tiny current of less than one billionth of the current that flows through a 100-watt light bulb - billions of electrons per second still flow. This is too many to discern individual electrons. The temperature was down at around a fifteen thousandth of a degree above absolute zero (i.e. at minus 273.135°C or 15 mK) before the scientists saw that the electric current consists of individual electrons.
At this low temperature, very fine structures, which the researchers had not expected, appear in the spectrum. "We could explain these new structures only by assuming that the tunnelling current is a granular medium and no longer homogeneous," says Ast, who heads the group working with the scanning tunnelling microscope. This is thus the first time that the full quantum nature of electronic transport in the scanning tunnelling microscope has shown itself.
The electric charge must therefore be quantized as well if this quantum mechanical phenomenon is to be fully explained. "The theory on which this is based was developed back at the beginning of the 1990s. Now that conceptual and practical issues relating to its application to scanning tunnelling microscopes have been solved, it is nice to see how consistently theory and experiment fit together," says Joachim Ankerhold from the University of Ulm, who contributed the theoretical basis.
In addition to a detailed theory, experiments of this type require an adapted laboratory environment which reduces external disturbances to a large extent. Since the end of 2012, a new precision laboratory has been in operation on the campus of the Max Planck Institutes in Stuttgart; it provides an almost disturbance-free laboratory environment for highly sensitive experiments such as the mK scanning tunnelling microscope.
The instrument is located in the precision laboratory in a box equipped with both acoustic and electromagnetic shielding on a vibration-decoupled concrete base. "We want to use it to venture into new, unknown territory - which we did very successfully with this experiment," says Klaus Kern, Director at the Max Planck Institute for Solid State Research.
Electrons have already demonstrated their quantum nature. As they are transported through quantum dots, for example, the current flow is specifically blocked so that the electrons appear individually. This effect became evident in the scanning tunnelling microscope simply by cooling it to extremely low temperatures, however. "The tunnel effect has definitely reached the quantum limit here," says team member Berthold Jäck. The researchers do not want to view this as a limitation, however. "These extremely low temperatures open up an unexpected richness of detail which allows us to understand superconductivity and light-matter interactions much better," says Christian Ast.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Prof. Klaus Kern
49-711-689-1660
Copyright © Max Planck Gesellschaft
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Physics
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Quantum Physics
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Imaging
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Superconductivity
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Tools
![]() Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
![]() The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
Quantum Dots/Rods
![]() A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
![]() IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
![]() Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
![]() NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() Bridging light and electrons January 12th, 2024
Bridging light and electrons January 12th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








