Home > Press > Physicists use lasers to capture first snapshots of rapid chemical bonds breaking
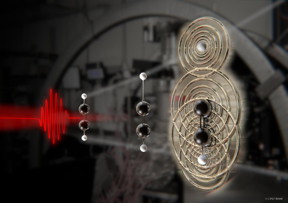 |
| An intense laser, represented in red, is used to affect an acetylene molecule -- composed of two hydrogen atoms, represented as white balls, and two carbon atoms, represented as black balls -- to strip out an electron and initiate the break up of the molecule. After nine femtoseconds, the laser drives the free electron back to the elongated molecule to create an image. Kansas State University researchers were able to decode the image and create the first real-time observation of a molecule breaking up. CREDIT ICFO-The Institute of Photonic Sciences and Scixel |
Abstract:
Lasers have successfully recorded a chemical reaction that happens as fast as a quadrillionth of a second, which could help scientists understand and control chemical reactions.
Physicists use lasers to capture first snapshots of rapid chemical bonds breaking
Manhattan, KS | Posted on October 21st, 2016The idea for using a laser to record a few femtoseconds of a molecule's extremely fast vibrations as it breaks apart came from Kansas State University physicists. Chii-Dong Lin, university distinguished professor of physics, and Anh-Thu Le, research associate professor in James R. Macdonald Laboratory, are part of an international collaborative project published in the Oct. 21 issue of Science.
"If you want to see something that happens very, very fast, you need a tool that can measure a very, very tiny time period," Lin said. "The only light available in femtosecond measurements is a laser."
A femtosecond is one-millionth of a billionth of a second, which is a million times shorter than a nanosecond. Until recently, there was no way to measure what happens during a chemical reaction in that short of a period.
Lin's research group made its first molecular movie of an oxygen molecule using lasers in 2012, but to record a larger molecule -- such as the four-atom acetylene molecule -- they needed a more advanced laser. After five years of collaboration with Jens Biegert's group from ICFO-The Institute of Photonic Sciences, a member of The Barcelona Institute of Science and Technology, Lin's idea became reality.
The international team used the molecule's own electrons to scatter the molecule -- a process called mid-infrared laser-induced electron diffraction, or LIED -- and capture snapshots of acetylene as it is breaking apart. An intense laser is used to affectan acetylene molecule -- composed of two hydrogen atoms and two carbon atoms -- to strip out an electron and initiate the breakup of the molecule. After nine femtoseconds, the laser drives the free electron back to the elongated molecule to create an image.
"Scientists will eventually be able to apply this tool in chemistry, biology and other physical sciences to look at different types of molecules and processes," Lin said.
According to Lin, acetylene's four-atom chemical structure provides multiple possibilities where the bonds could break. Being able to measure where and when those breaks occur can help researchers better understand chemical reactions, which Lin said will lead to better control of a reaction and is applicable to multiple areas of science.
"In order to control something, you have to know where it is first," Lin said. "If you throw a ball over a house, you can't see what happens to it, so you can't control it anymore. But if you have a way to see each second of the ball in the air, you can figure out why it ends up where it does and potentially change the way you throw it to control the outcome or to influence it in real time."
Lin's research group started working with Kansas State University distinguished professor emeritus Lew Cocke's research group in 2008 to conduct the first LIED experiment, which led to the current development. The initial experiments enabled the researchers to apply their theory to decode signals from electrons that produce the image. By decoding the image, the researchers accurately measured the molecule's new bond distances, which are smaller than one hundred-millionth of a centimeter.
"Since the snapshots, which are taken by the electrons, occur in a very strong laser field, it was thought to be nearly impossible to decode the electron information and measure the small distances," said Le, who provided critical decoding of the molecule's structure in the snapshot from Barcelona. "This is the first real-time observation of the breakup of a molecule within nine femtoseconds."
###
The international collaborators are from the ICFO-The Institute of Photonic Sciences, The Barcelona Institute of Science and Technology, and Catalan Institution for Research and Advanced Studies, all in Spain; the Leiden University in The Netherlands; The University of Kassel, the Center for Free-Electron Laser Science, Max Planck Institute for Nuclear Physics, Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt and University of Jena, all in Germany; and Aarhus University in Denmark.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Chii-Dong Lin
785-532-1617
Copyright © Kansas State University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Chemistry
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Imaging
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








