Home > Press > Perpetual 'ice water': Stable solid-liquid state revealed in nanoparticles: Gallium nanoparticles that are both solid and liquid are stable over a range of 1000 degrees Fahrenheit
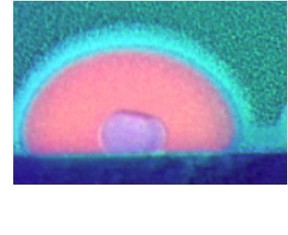 |
| A side, false-color view of a solid gallium core coexisting within a liquid gallium nanoparticle. These novel nanoparticles show unique interactions with light and electrons at the atomic scale, which could be exploited by a field called plasmonics for new light-based technologies. CREDIT: April Brown, Duke University |
Abstract:
Imagine pouring a glass of ice water and having the ice cubes remain unchanged hours later, even under a broiler's heat or in the very back corner of the freezer.
Perpetual 'ice water': Stable solid-liquid state revealed in nanoparticles: Gallium nanoparticles that are both solid and liquid are stable over a range of 1000 degrees Fahrenheit
Durham, NC | Posted on August 5th, 2016That's fundamentally the surprising discovery recently made by an international group of researchers led by an electrical engineering professor at Duke University in a paper published online in Nature Matter on July 25, 2016. But instead of a refreshing mixture of H2O in a pint glass, the researchers were working with the chemical element gallium on a nanoscopic scale.
Gallium is a soft, silvery bluish metal at room temperature. Raise the heat to 86 degrees Fahrenheit, however, and it melts. Drop the temperature to subzero levels, and it becomes hard and brittle. But when gallium nanoparticles sit on top of a sapphire surface, they form a solid core surrounded by a liquid outer layer. The discovery marks the first time that this stable phase coexistence phenomenon at the nanoscale has ever been directly observed.
"This odd combination of a liquid and solid state existing together has been predicted theoretically and observed indirectly in other materials in narrow bands of specific temperatures," said April Brown, the John Cocke Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering at Duke. "But this finding was very unexpected, especially because of its stability over such a large temperature range."
The temperature range Brown is referring to covers more than 1,000 degrees Fahrenheit, all the way from -135 to 980 degrees.
"At a fundamental level, this finding reveals the need to reconsider all our presumptions about solid-liquid equilibrium," wrote Andrés Aguado, professor of theoretical, atomic and optical physics at the University of Valladolid in Spain, in a News and Views piece appearing in the same edition of Nature Matter. "At a more applied level, the results hold much promise for future nanotechnology applications."
Gallium is an important element in electronics and is used in microwave circuits, high-speed switching circuits and infrared circuits. The discovery of this novel part-solid, part-liquid nanoparticle phase could be useful in ultraviolet sensors, molecular sensing devices and enhanced photodetectors.
Brown hopes this work is just the tip of the iceberg, as she is planning on creating a facility at Duke to investigate what other nanoparticles might have similar unexpected phase qualities.
###
The research was conducted in conjunction with researchers at the Institute of Nanotechnology-CNR-Italy, the University of Western Australia, the University of Melbourne and Johannes Kepler University Linz.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Ken Kingery
919-660-8414
Copyright © Duke University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Physics
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Sensors
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








