Home > Press > New lithium-oxygen battery greatly improves energy efficiency, longevity: New chemistry could overcome key drawbacks of lithium-air batteries
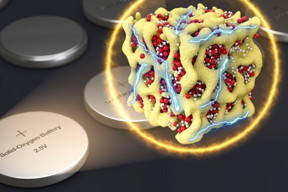 |
| In a new concept for battery cathodes, nanometer-scale particles made of lithium and oxygen compounds (depicted in red and white) are embedded in a sponge-like lattice (yellow) of cobalt oxide, which keeps them stable. The researchers propose that the material could be packaged in batteries that are very similar to conventional sealed batteries yet provide much more energy for their weight.
Courtesy of the researchers |
Abstract:
Lithium-air batteries are considered highly promising technologies for electric cars and portable electronic devices because of their potential for delivering a high energy output in proportion to their weight. But such batteries have some pretty serious drawbacks: They waste much of the injected energy as heat and degrade relatively quickly. They also require expensive extra components to pump oxygen gas in and out, in an open-cell configuration that is very different from conventional sealed batteries.
New lithium-oxygen battery greatly improves energy efficiency, longevity: New chemistry could overcome key drawbacks of lithium-air batteries
Cambridge, MA | Posted on July 26th, 2016But a new variation of the battery chemistry, which could be used in a conventional, fully sealed battery, promises similar theoretical performance as lithium-air batteries, while overcoming all of these drawbacks.
The new battery concept, called a nanolithia cathode battery, is described in the journal Nature Energy in a paper by Ju Li, the Battelle Energy Alliance Professor of Nuclear Science and Engineering at MIT; postdoc Zhi Zhu; and five others at MIT, Argonne National Laboratory, and Peking University in China.
One of the shortcomings of lithium-air batteries, Li explains, is the mismatch between the voltages involved in charging and discharging the batteries. The batteries' output voltage is more than 1.2 volts lower than the voltage used to charge them, which represents a significant power loss incurred in each charging cycle. "You waste 30 percent of the electrical energy as heat in charging. ... It can actually burn if you charge it too fast," he says.
Staying solid
Conventional lithium-air batteries draw in oxygen from the outside air to drive a chemical reaction with the battery's lithium during the discharging cycle, and this oxygen is then released again to the atmosphere during the reverse reaction in the charging cycle.
In the new variant, the same kind of electrochemical reactions take place between lithium and oxygen during charging and discharging, but they take place without ever letting the oxygen revert to a gaseous form. Instead, the oxygen stays inside the solid and transforms directly between its three redox states, while bound in the form of three different solid chemical compounds, Li2O, Li2O2, and LiO2, which are mixed together in the form of a glass. This reduces the voltage loss by a factor of five, from 1.2 volts to 0.24 volts, so only 8 percent of the electrical energy is turned to heat. "This means faster charging for cars, as heat removal from the battery pack is less of a safety concern, as well as energy efficiency benefits," Li says.
This approach helps overcome another issue with lithium-air batteries: As the chemical reaction involved in charging and discharging converts oxygen between gaseous and solid forms, the material goes through huge volume changes that can disrupt electrical conduction paths in the structure, severely limiting its lifetime.
The secret to the new formulation is creating minuscule particles, at the nanometer scale (billionths of a meter), which contain both the lithium and the oxygen in the form of a glass, confined tightly within a matrix of cobalt oxide. The researchers refer to these particles as nanolithia. In this form, the transitions between LiO2, Li2O2, and Li2O can take place entirely inside the solid material, he says.
The nanolithia particles would normally be very unstable, so the researchers embedded them within the cobalt oxide matrix, a sponge-like material with pores just a few nanometers across. The matrix stabilizes the particles and also acts as a catalyst for their transformations.
Conventional lithium-air batteries, Li explains, are "really lithium-dry oxygen batteries, because they really can't handle moisture or carbon dioxide," so these have to be carefully scrubbed from the incoming air that feeds the batteries. "You need large auxiliary systems to remove the carbon dioxide and water, and it's very hard to do this." But the new battery, which never needs to draw in any outside air, circumvents this issue.
No overcharging
The new battery is also inherently protected from overcharging, the team says, because the chemical reaction in this case is naturally self-limiting -- when overcharged, the reaction shifts to a different form that prevents further activity. "With a typical battery, if you overcharge it, it can cause irreversible structural damage or even explode," Li says. But with the nanolithia battery, "we have overcharged the battery for 15 days, to a hundred times its capacity, but there was no damage at all."
In cycling tests, a lab version of the new battery was put through 120 charging-discharging cycles, and showed less than a 2 percent loss of capacity, indicating that such batteries could have a long useful lifetime. And because such batteries could be installed and operated just like conventional solid lithium-ion batteries, without any of the auxiliary components needed for a lithium-air battery, they could be easily adapted to existing installations or conventional battery pack designs for cars, electronics, or even grid-scale power storage.
Because these "solid oxygen" cathodes are much lighter than conventional lithium-ion battery cathodes, the new design could store as much as double the amount of energy for a given cathode weight, the team says. And with further refinement of the design, Li says, the new batteries could ultimately double that capacity again.
All of this is accomplished without adding any expensive components or materials, according to Li. The carbonate they use as the liquid electrolyte in this battery "is the cheapest kind" of electrolyte, he says. And the cobalt oxide component weighs less than 50 percent of the nanolithia component. Overall, the new battery system is "very scalable, cheap, and much safer" than lithium-air batteries, Li says.
The team expects to move from this lab-scale proof of concept to a practical prototype within about a year.
###
The research team included MIT research scientists Akihiro Kushima and Zongyou Yin; Lu Qi of Peking University; and Khalil Amine and Jun Lu of Argonne National Laboratory in Illinois. The work was supported by the National Science Foundation and the U.S. Department of Energy.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Karl-Lydie Jean-Baptiste
617-253-1682
Copyright © Massachusetts Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Paper: “Anion-redox nanolithia cathodes for Li-ion batteries”:
Paper: “Anion-redox nanolithia cathodes for Li-ion batteries”:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Laboratories
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
![]() Three-pronged approach discerns qualities of quantum spin liquids November 17th, 2023
Three-pronged approach discerns qualities of quantum spin liquids November 17th, 2023
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








