Home > Press > 'Breaking me softly:' UCF fiber findings featured in Nature
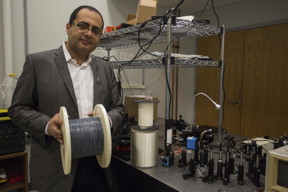 |
| "What we expected to see happen is NOT what happened," said UCF Associate Professor Ayman Abouraddy, whose Breaking Me Softly technique is described in the Nature paper. "While we thought the core material would snap into two large pieces, instead it broke into many equal-sized pieces." CREDIT: UCF |
Abstract:
A finding by a University of Central Florida researcher that unlocks a means of controlling materials at the nanoscale and opens the door to a new generation of manufacturing is featured online today in the journal Nature.
'Breaking me softly:' UCF fiber findings featured in Nature
Orlando, FL | Posted on June 7th, 2016Using a pair of pliers in each hand and gradually pulling taut a piece of glass fiber coated in plastic, associate professor Ayman Abouraddy found that something unexpected and never before documented occurred -- the inner fiber fragmented in an orderly fashion.
"What we expected to see happen is NOT what happened," he said. "While we thought the core material would snap into two large pieces, instead it broke into many equal-sized pieces."
He referred to the technique in the Nature article title as "Breaking Me Softly."
The process of pulling fibers to force the realignment of the molecules that hold it them together, known as cold drawing, has been the standard for mass production of flexible fibers like plastic and nylon for most of the last century.
Abouraddy and his team have shown that the process may also be applicable to multi-layered materials, a finding that could lead to the manufacturing of a new generation of materials with futuristic attributes.
"Advanced fibers are going to be pursuing the limits of anything a single material can endure today," Abouraddy said.
For example, packaging together materials with optical and mechanical properties along with sensors that could monitor such vital sign as blood pressure and heart rate would make it possible to make clothing capable of transmitting vital data to a doctor's office via the Internet.
The ability to control breakage in a material is critical to developing computerized processes for potential manufacturing, said Yuanli Bai, a fracture mechanics specialist in UCF's College of Engineering and Computer Science.
Abouraddy contacted Bai, who is a co-author on the paper, about three years ago and asked him to analyze the test results on a wide variety of materials, including silicon, silk, gold and even ice.
He also contacted Robert S. Hoy, a University of South Florida physicist who specializes in the properties of materials like glass and plastic, for a better understanding of what he found.
Hoy said he had never seen the phenomena Abouraddy was describing, but that it made great sense in retrospect.
The research takes what has traditionally been a problem in materials manufacturing and turned it into an asset, Hoy said.
"Dr. Abouraddy has found a new application of necking" - a process that occurs when cold drawing causes non-uniform strain in a material, Hoy said. "Usually you try to prevent necking, but he exploited it to do something potentially groundbreaking."
The necking phenomenon was discovered decades ago at DuPont and ushered in the age of textiles and garments made of synthetic fibers. Abouraddy said that cold-drawing is what makes synthetic fibers like nylon and polyester useful. While the parts of those fibers are individually brittle, once cold-drawn, the fibers toughen up and become useful in everyday commodities. This discovery at DuPont at the end of the 1920s ushered in the age of textiles and garments made of synthetic fibers.
Only recently have fibers made of multiple materials become possible, he said. That research will be the centerpiece of a $317 Million U.S. Department of Defense program focused on smart fibers that Abouraddy and UCF will assist with. The Revolutionary Fibers and Textiles Manufacturing Innovation Institute (RFT-MII), led by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, will incorporate research findings published in the Nature paper, Abouraddy said.
The implications for manufacturing of the smart materials of the future are vast.
By controlling the mechanical force used to pull the fiber and therefore controlling the breakage patterns, materials can be developed with customized properties allowing them to interact with each other and eternal forces such as the sun (for harvesting energy) and the internet in customizable ways.
A co-author on the paper, Ali P. Gordon, an associate professor in the Department of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering and director of UCF's Mechanical of Materials Research Group said that the finding is significant because it shows that by carefully controlling the loading condition imparted to the fiber, materials can be developed with tailored performance attributes.
"Processing-structure-property relationships need to be strategically characterized for complex material systems. By combining experiments, microscopy, and computational mechanics, the physical mechanisms of the fragmentation process were more deeply understood," Gordon said.
###
Abouraddy teamed up with seven UCF scientists from the College of Optics & Photonics and the College of Engineering & Computer Science (CECS) to write the paper. Additional authors include one researcher each from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Nanyang Technological University in Singapore and the University of South Florida.
Authors are Abouraddy, graduate students Joshua J. Kaufman, Guangming Tao and Soroush Shabahang from CREOL- The College of Optics and Photonics at UCF, Yangyang Qiao, Yuanli Bai, Ali P. Gordon and Thomas Bouchenot from the College of Engineering & Computer Science at UCF, Robert S. Hoy from the University of South Florida, Yoel Fink from MIT and Lei Wei from Nanyang University, Singapore.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Barbara Abney
407-823-5139
Copyright © University of Central Florida
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Energy
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() Charged “molecular beasts” the basis for new compounds: Researchers at Leipzig University use “aggressive” fragments of molecular ions for chemical synthesis November 3rd, 2023
Charged “molecular beasts” the basis for new compounds: Researchers at Leipzig University use “aggressive” fragments of molecular ions for chemical synthesis November 3rd, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








