Home > Press > A fast solidification process makes material crackle
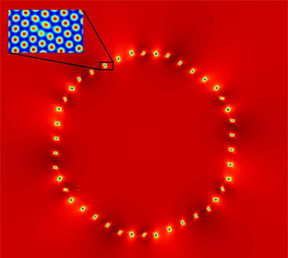 |
| The computational density field shows a circular solid crystal with a different orientation in relation to the surrounding solid material. The blue areas seen on the edges are lattice defects caused by differences in orientations. One of them has been magnified in order to show the defect in the periodic structure of the lattice. CREDIT: Aalto University |
Abstract:
What does it sound like when liquids solidify very fast?
Researchers from the Centre of Excellence in Computational Nanoscience at Aalto University and their colleagues at Brown University and the University of California, Irvine, have developed a theory that answers this question by combining for the first time the understanding of vibrations in solid material and the solidification of liquid at a microscopic level. The results were published in the renowned scientific publication Physical Review Letters in January.
A fast solidification process makes material crackle
Aalto, Finland | Posted on February 8th, 2016'Earlier theories have focused on slow solidification. It is effectively diffusion in which the movement of atoms is slow and random. When solidification is fast, the atoms do not move only randomly, but the reaction is as if they had been compressed together. What our model can predict is the sound wave that is formed when the compression relaxes,' describes doctoral candidate Vili Heinonen.
Liquids usually solidify so slowly that no sound is created. When the process is fast, as it is when supercool water freezes, large defects are formed in the lattice structure of the material. According to Vili Heinonen, the wave formed when the defects relax resembles a kind of crackling. Effectively, the human ear cannot hear the sound, as supercool liquids that occur in nature are small droplets.
In addition to the crackling, the model also reveals a lot more.
'It helps us understand and predict the defects that are formed in materials - especially in metals - when they solidify. Also, materials often have different interfaces that are not always compatible. By understanding these defects we can also understand better why metals produced in certain temperatures have certain properties - and whether we can do something about it,' Heinonen explains.
The researchers proved the functionality of the model by analysing vibrations theoretically and computationally. In the computational test, the model was compared with predictions given by earlier theories, and it was demonstrated that the properties of the new theory are vitally important when we want to understand how, for example, the microscopic structure of metals changes in high temperatures. In addition to enabling control over the process of metal production, understanding these matters could in future enable a cheap method to produce intelligent nanostructures.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Vili Heinonen
358-504-332-834
Copyright © Aalto University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Physics
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Molecular Nanotechnology
![]() Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
![]() Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








