Home > Press > Simplifying solar cells with a new mix of materials: Berkeley Lab-led research team creates a high-efficiency device in 7 steps
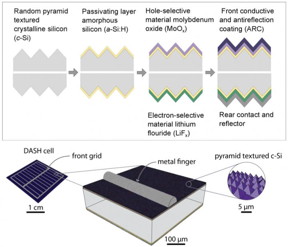 |
| In this illustration, the top images show a cross-section of a solar cell design, called DASH, that uses a combination of moly oxide and lithium fluoride. This combination of materials allows the device to achieve high efficiency in converting sunlight to energy without the need for a process known as doping. The bottom images shows the dimensions of the DASH solar cell components.>BR> CREDIT: Nature Energy: 10.1038/nenergy.2015.31 |
Abstract:
An international research team has simplified the steps to create highly efficient silicon solar cells by applying a new mix of materials to a standard design. Arrays of solar cells are used in solar panels to convert sunlight to electricity.
Simplifying solar cells with a new mix of materials: Berkeley Lab-led research team creates a high-efficiency device in 7 steps
Berkeley, CA | Posted on January 29th, 2016The special blend of materials--which could also prove useful in semiconductor components--eliminates the need for a process known as doping that steers the device's properties by introducing foreign atoms to its electrical contacts. This doping process adds complexity to the device and can degrade its performance.
"The solar cell industry is driven by the need to reduce costs and increase performance," said James Bullock, the lead author of the study, published this week in Nature Energy. Bullock participated in the study as a visiting researcher at the U.S. Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and UC Berkeley.
"If you look at the architecture of the solar cell we made, it is very simple," said Bullock, of Australian National University (ANU). "That simplicity can translate to reduced cost."
Other scientists from Berkeley Lab, UC Berkeley, ANU and The Swiss Federal Institute of Technology of Lausanne (EPFL) also participated in the study.
Bullock added, "Conventional silicon solar cells use a process called impurity doping, which does bring about a number of limitations that are making further progress increasingly difficult."
Most of today's solar cells use crystalline silicon wafers. The wafer itself, and sometimes the layers deposited on the wafer, are doped with atoms that either have electrons to spare when they bond with silicon atoms, or alternatively generate electron deficiencies, or "holes." In both cases, this doping enhances electrical conductivity.
In these devices, two types of dopant atoms are required at the solar cell's electrical contacts to regulate how the electrons and holes travel in a solar cell so that sunlight is efficiently converted to electrical current that flows out of the cell.
Crystalline silicon-based solar cells with doped contacts can exceed 20 percent efficiency--meaning more than 20 percent of the sun's energy is converted to electricity. A dopant-free silicon cell had not previously exceeded 14 percent efficiency.
The new study, though, demonstrated a dopant-free silicon cell, referred to as a DASH cell (dopant free asymmetric heterocontact), with an average efficiency above 19 percent. This increased efficiency is a product of the new materials and a simple coating process for layers on the top and bottom of the device. Researchers showed it's possible to create their solar cell in just seven steps.
In this study, the research team used a crystalline silicon core (or wafer) and applied layers of dopant-free type of silicon called amorphous silicon.
Then, they applied ultrathin coatings of a material called molybdenum oxide, also known as moly oxide, at the sun-facing side of the solar cell, and lithium fluoride at the bottom surface. The two layers, having thicknesses of tens of nanometers, act as dopant-free contacts for holes and electrons, respectively.
"Moly oxide and lithium fluoride have properties that make them ideal for dopant-free electrical contacts," said Ali Javey, program leader of Electronic Materials at Berkeley Lab and a professor of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences at UC Berkeley.
Both materials are transparent, and they have complementary electronic structures that are well-suited for solar cells.
"They were previously explored for other types of devices, but they were not carefully explored by the crystalline silicon solar cell community," said Javey, the lead senior author of the study.
Javey noted that his group had discovered the utility of moly oxide as an efficient hole contact for crystalline silicon solar cells a couple of years ago. "It has a lot of defects, and these defects are critical and important for the arising properties. These are good defects," he said.
Stefaan de Wolf, another author who is team leader for crystalline silicon research at EPFL in Neuchâtel, Switzerland, said, "We have adapted the technology in our solar cell manufacturing platform at EPFL and found out that these moly oxide layers work extremely well when optimized and used in combination with thin amorphous layer of silicon on crystalline wafers. They allow amazing variations of our standard approach."
In the study, the team identified lithium fluoride as a good candidate for electron contacts to crystalline silicon coated with a thin amorphous layer. That layer complements the moly oxide layer for hole contacts.
The team used a room-temperature technique called thermal evaporation to deposit the layers of lithium fluoride and moly oxide for the new solar cell. There are many other materials that the research teams hopes to test to see if they can improve the cell's efficiency.
Javey said there is also promise for adapting the material mix used in the solar cell study to improve the performance of semiconductor transistors. "There's a critical need to reduce the contact resistance in transistors so we're trying to see if this can help."
###
Some off the work in this study was performed at The Molecular Foundry, a DOE Office of Science User Facility at Berkeley Lab.
This work was supported by the DOE Office of Science, Bay Area Photovoltaics Consortium (BAPVC); the Joint Center for Artificial Photosynthesis, a DOE Energy Innovation Hub; Office fédéral de l'énergie (OFEN); the Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA) and the CSEM PV-center.
####
About Berkeley Lab
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory addresses the world's most urgent scientific challenges by advancing sustainable energy, protecting human health, creating new materials, and revealing the origin and fate of the universe. Founded in 1931, Berkeley Lab's scientific expertise has been recognized with 13 Nobel prizes. The University of California manages Berkeley Lab for the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science. For more, visit www.lbl.gov.
The DOE Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Glenn Roberts Jr.
510-486-5582
Copyright © Berkeley Lab
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Laboratories
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
![]() Three-pronged approach discerns qualities of quantum spin liquids November 17th, 2023
Three-pronged approach discerns qualities of quantum spin liquids November 17th, 2023
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Chip Technology
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Energy
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() Charged “molecular beasts” the basis for new compounds: Researchers at Leipzig University use “aggressive” fragments of molecular ions for chemical synthesis November 3rd, 2023
Charged “molecular beasts” the basis for new compounds: Researchers at Leipzig University use “aggressive” fragments of molecular ions for chemical synthesis November 3rd, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








