Home > Press > Coming to a monitor near you: A defect-free, molecule-thick film
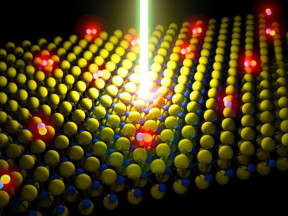 |
| This is a schematic of a laser beam energizing a monolayer semiconductor made up of molybdenum disulfide (MoS2). The red glowing dots are particles excited by the laser.
Image by Der-Hsien Lien |
Abstract:
An emerging class of atomically thin materials known as monolayer semiconductors has generated a great deal of buzz in the world of materials science. Monolayers hold promise in the development of transparent LED displays, ultra-high efficiency solar cells, photo detectors and nanoscale transistors. Their downside? The films are notoriously riddled with defects, killing their performance.
Coming to a monitor near you: A defect-free, molecule-thick film
Berkeley, CA | Posted on November 29th, 2015But now a research team, led by engineers at the University of California, Berkeley, and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, has found a simple way to fix these defects through the use of an organic superacid. The chemical treatment led to a dramatic 100-fold increase in the material's photoluminescence quantum yield, a ratio describing the amount of light generated by the material versus the amount of energy put in. The greater the emission of light, the higher the quantum yield and the better the material quality.
The researchers enhanced the quantum yield for molybdenum disulfide, or MoS2, from less than 1 percent up to 100 percent by dipping the material into a superacid called bistriflimide, or TFSI.
Their findings, to be published in the Nov. 27 issue of Science, opens the door to the practical application of monolayer materials, such as MoS2, in optoelectronic devices and high-performance transistors. MoS2 is a mere seven-tenths of a nanometer thick. For comparison, a strand of human DNA is 2.5 nanometers in diameter.
"Traditionally, the thinner the material, the more sensitive it is to defects," said principal investigator Ali Javey, UC Berkeley professor of electrical engineering and computer sciences and a faculty scientist at Berkeley Lab. "This study presents the first demonstration of an optoelectronically perfect monolayer, which previously had been unheard of in a material this thin."
The researchers looked to superacids because, by definition, they are solutions with a propensity to "give" protons, often in the form of hydrogen atoms, to other substances. This chemical reaction, called protonation, has the effect of filling in for the missing atoms at the site of defects as well as removing unwanted contaminants stuck on the surface, the researchers said.
Co-lead authors of the paper are UC Berkeley Ph.D. student Matin Amani, visiting Ph.D. student Der-Hsien Lien and postdoctoral fellow Daisuke Kiriya.
They noted that scientists have been pursuing monolayer semiconductors because of their low absorption of light and their ability to withstand twists, bends and other extreme forms of mechanical deformation, which can enable their use in transparent or flexible devices.
MoS2, specifically, is characterized by molecular layers held together by van der Waals forces, a type of atomic bonding between each layer that is atomically sharp. An added benefit of having a material that is so thin is that it is highly electrically tunable. For applications such as LED displays, this feature may allow devices to be made where a single pixel could emit a wide range of colors rather than just one by varying the amount of voltage applied.
The lead authors added that the efficiency of an LED is directly related to the photoluminescence quantum yield so, in principle, one could develop high-performance LED displays that are transparent when powered off and flexible using the "perfect" optoelectronic monolayers produced in this study.
This treatment also has revolutionary potential for transistors. As devices in computer chips get smaller and thinner, defects play a bigger role in limiting their performance.
"The defect-free monolayers developed here could solve this problem in addition to allowing for new types of low-energy switches," said Javey.
###
Xiang Zhang and Eli Yablonovitch, faculty members with joint appointments at UC Berkeley's College of Engineering and Berkeley Lab, co-authored this paper. Other co-authors include researchers from National Taiwan University, the University of Texas and the U.S. Army Research Laboratory in Maryland.
The work was funded by the U.S. Department of Energy, the National Science Foundation Center for Energy Efficient Electronics and Science at UC Berkeley, Samsung and the Center for Low Energy System Technology.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Sarah Yang
510-643-7741
Copyright © University of California, Berkeley
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Laboratories
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
![]() Three-pronged approach discerns qualities of quantum spin liquids November 17th, 2023
Three-pronged approach discerns qualities of quantum spin liquids November 17th, 2023
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chip Technology
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Sensors
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Energy
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() Charged “molecular beasts” the basis for new compounds: Researchers at Leipzig University use “aggressive” fragments of molecular ions for chemical synthesis November 3rd, 2023
Charged “molecular beasts” the basis for new compounds: Researchers at Leipzig University use “aggressive” fragments of molecular ions for chemical synthesis November 3rd, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








